EmSAT Achieve Exam > EmSAT Achieve Tests > Physics for EmSAT Achieve > Test: Magnetism - EmSAT Achieve MCQ
Test: Magnetism - EmSAT Achieve MCQ
Test Description
10 Questions MCQ Test Physics for EmSAT Achieve - Test: Magnetism
Test: Magnetism for EmSAT Achieve 2025 is part of Physics for EmSAT Achieve preparation. The Test: Magnetism questions and answers have been
prepared according to the EmSAT Achieve exam syllabus.The Test: Magnetism MCQs are made for EmSAT Achieve 2025 Exam. Find important
definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests for Test: Magnetism below.
Solutions of Test: Magnetism questions in English are available as part of our Physics for EmSAT Achieve for EmSAT Achieve & Test: Magnetism solutions in
Hindi for Physics for EmSAT Achieve course. Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock
test series for EmSAT Achieve Exam by signing up for free. Attempt Test: Magnetism | 10 questions in 10 minutes | Mock test for EmSAT Achieve preparation | Free important questions MCQ to study Physics for EmSAT Achieve for EmSAT Achieve Exam | Download free PDF with solutions
Detailed Solution for Test: Magnetism - Question 1
Test: Magnetism - Question 2
How many of the following materials can be attracted by a magnet?
- Plastic
- Carbon
- Aluminium
- Stainless Steel
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
Detailed Solution for Test: Magnetism - Question 2
Test: Magnetism - Question 3
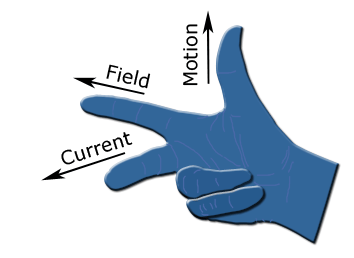
In Fleming's left rule, the middle finger represents ________________.
Detailed Solution for Test: Magnetism - Question 3
Test: Magnetism - Question 4
What does the forefinger indicate in the Fleming's right hand rule?
Detailed Solution for Test: Magnetism - Question 4
Detailed Solution for Test: Magnetism - Question 5
Detailed Solution for Test: Magnetism - Question 6
Detailed Solution for Test: Magnetism - Question 7
Test: Magnetism - Question 8
A natural magnet is an ore of which of the following chemical compound?
Detailed Solution for Test: Magnetism - Question 8
Test: Magnetism - Question 9
When an electric current passes through a solenoid, it acts as a/an_______.
Detailed Solution for Test: Magnetism - Question 9
Detailed Solution for Test: Magnetism - Question 10
|
215 videos|402 docs|221 tests
|
Information about Test: Magnetism Page
In this test you can find the Exam questions for Test: Magnetism solved & explained in the simplest way possible.
Besides giving Questions and answers for Test: Magnetism, EduRev gives you an ample number of Online tests for practice