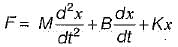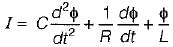Test: Modelling of Control Systems- 2 - Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Modelling of Control Systems- 2
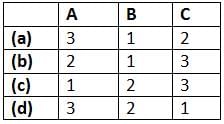
Match List - I (Control system components) with List - II (Principle of operation) and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:
List - I
A. Synchronous
B. Potentiometer
C. Tachometer
List - lI
1. Mechanical displacement into electrical energy.
2. Angular position of a shaft into an electrical signal.
3. Electrical output proportional to speed.
Codes:
List - I
A. Synchronous
B. Potentiometer
C. Tachometer
List - lI
1. Mechanical displacement into electrical energy.
2. Angular position of a shaft into an electrical signal.
3. Electrical output proportional to speed.
Codes:

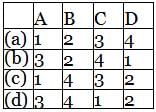
Match List - I (Control System Components) with List - II (Applications) and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:
List - I
A. Stepper Motors
B. Synchros
C. Servomotors
D. Potentiometer
List - II
1. Radars, electromechanical actuators.
2. Displacement transducer
3. Printers, Watches
4. Detectors and encoders
Codes:
List - I
A. Stepper Motors
B. Synchros
C. Servomotors
D. Potentiometer
List - II
1. Radars, electromechanical actuators.
2. Displacement transducer
3. Printers, Watches
4. Detectors and encoders
Codes:

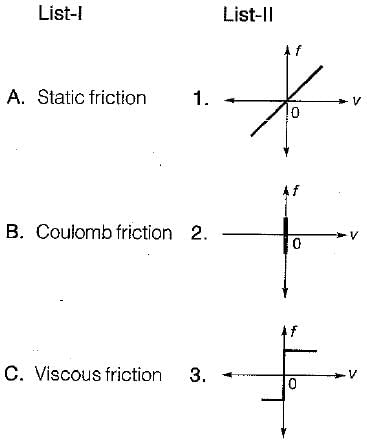
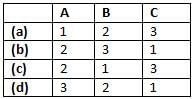
Match List - I (Types of friction) with List - II (Corresponding frictional force vs Velocity curve) and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:
Assertion (A): D’Alembert’s principle states that “for any- body, the algebraic sum of externally applied forces and the forces resisting motion in any given direction is zero.
”Reason (R): D’Alembert principle is used in writing the equation of motion of mechanical systems.
Assertion (A): When two time constant elements are cascaded interactively, the overall transfer function of such an arrangement is the product of two individual transfer functions.
Reason (R): There is loading effect present in such an arrangement.
Assertion (A): An a.c. servomotor used in control system applications must have high starting torque and low inertia.
Reason (R): A large value of rotor diameter and small axial length gives a higher value of starting torque and a low value of inertia.
Assertion (A): When the rotor of the synchro is inclined along any one of the stator axis completely, then this position is called electrical zero position.
Reason (R): When the rotor of the synchro is inclined along any one of the stator axis completely, then maximum voltage will be induced in that winding and almost zero voltage will be induced in the other two windings.
Assertion (A): Stepper motors can be used for speed control.
Reason (R): The motor speed is proportional to the rate of command pulses.
The transfer function of a tachometer is of the form
In force-current analogy stiffness constant K is analogous to
In liquid level systems, the units of capacitance of a tank is