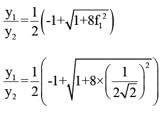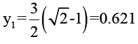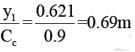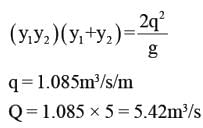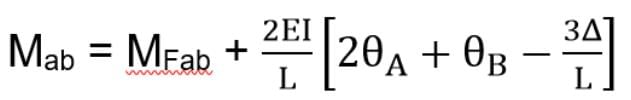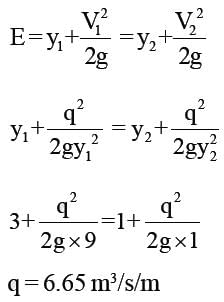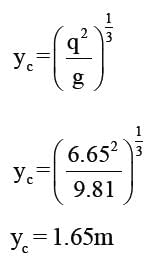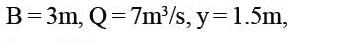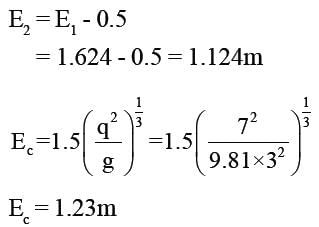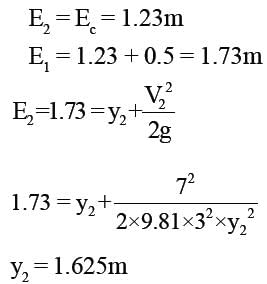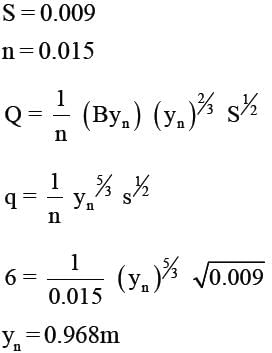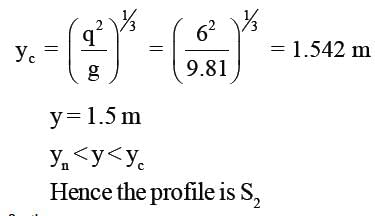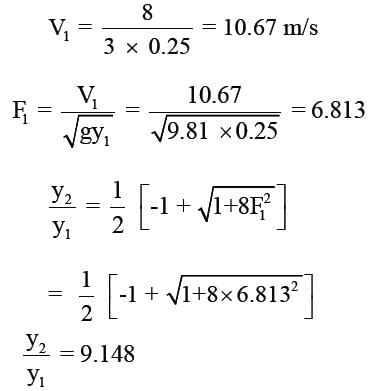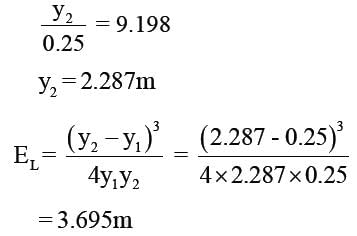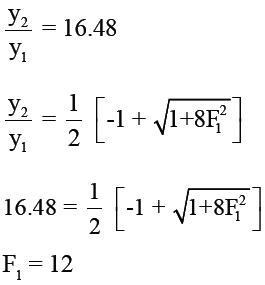Test: Open Channel Flow - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test GATE Civil Engineering (CE) 2026 Mock Test Series - Test: Open Channel Flow
A partially open sluice gate discharges water into a rectangular channel. The tail water depth in the channel is 3m and Froude number is 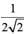 . If a free hydraulic jump is to be formed at downstream of the sluice gate at vena contracta of the jet coming out from the sluice gate, the sluice gate opening should be (Coefficient of contraction Cc = 0.9)
. If a free hydraulic jump is to be formed at downstream of the sluice gate at vena contracta of the jet coming out from the sluice gate, the sluice gate opening should be (Coefficient of contraction Cc = 0.9)
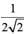 . If a free hydraulic jump is to be formed at downstream of the sluice gate at vena contracta of the jet coming out from the sluice gate, the sluice gate opening should be (Coefficient of contraction Cc = 0.9)
. If a free hydraulic jump is to be formed at downstream of the sluice gate at vena contracta of the jet coming out from the sluice gate, the sluice gate opening should be (Coefficient of contraction Cc = 0.9)On sag (or valley) curves the available sight distance is determined based on :
The sequent depths in a hydraulic jump formed in a 5m wide rectangular channel are 0.2m and 1m. The discharge in the channel is:
The number of simultaneous equations to be solved in the slope deflection method, is equal to :
A rectangular channel carries a certain flow for which the alternate depths are found to be 3m and 1m. The critical depth (in m) for this flow is:
In a triangular channel, the critical depth is 2m. The corresponding least possible specific energy is:
If the Froude number of flow in a rectangular channel at a depth of flow of y0 is F0, then what is yc/y0 equal to?
A rectangular channel 3m wide carries uniform flow of water at a rate of 7 cumec/sec at a depth of 1.5m. If there is a local rise of 0.5m in the bed, calculate the change in upstream depth of flow?
A wide rectangular channel carries discharge of 6 m3/s per meter width. The channel has a bed slope of 0.009 and Manning's roughness coefficient, n = 0.015. At a certain section of the channel, the flow depth is 1.5m. What gradually varied flow profile exist at this section ?
In a hydraulic jump occurring in a rectangular channel of 3m width, the discharge is 8 m3/s, and the depth of flow before jump is 0.25m. Find the energy loss in the jump ?
The sequent depth ratio in a hydraulic jump formed in a horizontal rectangular channel is 16.48. The Froude number of the super critical stream is :
A mild slope channel enters a lake with a sudden drop in bed. If the depth of water in the lake measured above the channel bed at its outlet yL is greater than the critical depth, then the depth of flow in the canal at the outlet yd :
Water emerges from an ogee spillway with velocity 13.72 m/s and depth = 0.3 m at its toe. The tail water depth required to form a hydraulic jump at the toe is
The ratio of unconfined compressive strength of an undisturbed sample of soil to that of a remoulded sample, at the same water content, is known as :
In a channel the bed slope changes from mild slope to steep slope. The resulting GVF profiles are :
In a wide river the depth of flow at a section is 3m, S0 = 1 in 5000 and q = 3m3/s per meter width. If the Chezy formula with C = 70 is used, the water surface slope relative to the bed at the section is:
A triangular channel of side slope 3:1 carries water at a flow rate of 10m3 /s. If the depth of the flow is 1.32m and the channel is laid on slope of 0.0018, find Manning’s n.
In an open channel with a rectangular cross-section, the flow depth is doubled while keeping the channel width and slope constant. Assuming the flow remains subcritical and the Manning's roughness coefficient remains unchanged, the new discharge will:
|
31 docs|280 tests
|