Test: Plain Carbon Steel, Iron Carbon Equilibrium Diagram & Cast Iron - 1 - Mechanical Engineering MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test GATE Mechanical (ME) Mock Test Series 2025 - Test: Plain Carbon Steel, Iron Carbon Equilibrium Diagram & Cast Iron - 1
The true strain for a low carbon steel bar which is doubled in length by forging is
Match List I with List II and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:
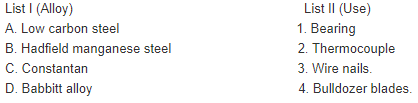
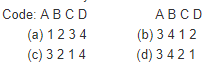
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Match List I (Alloy) with List II (Application) and select the correct answer using the codes given below the Lists:
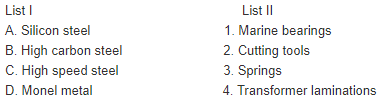
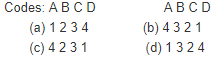
For the pipe fitting like elbow, tee, union etc. which of the following is preferred?
Increasing carbon content in steel, _________ ultimate strength and ____ ductility of steel.
Presence of hydrogen in steel causes
Match List I (Percentage of carbon content in plain carbon steel) with List II (Application) and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:
Match List-I (Fe-Fe3C Phase Diagram Characteristic) with List-II (Phase) and select the correct answer using the code given below the Lists:
Consider the following statements:
1. From design considerations, it is always advantageous to place cast iron ribs on thetension side rather than on the compression side.
2. Cast iron is an excellent choice for machine tool guides and frames.
3. Cast iron parts have low notch sensitivity.
Which of these statements are correct?
Which of the following display properties similar to that of steel
1. Black-heart cast iron
2. White-heart cast iron
3. Gray cast iron
4. Pig iron
Assertion (A): Fracture surface of grey cast iron is dark.
Reason (R): Failure takes place along the weak cementite plates.
Addition of magnesium to cast iron increases its
Eutectoid reaction occurs at
An iron-carbon binary alloy has 0.5% C by weight. What is this alloy called?
Match List I with List II and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:
Consider the following statements:
Addition of silicon to cast iron
1. Promotes graphite module formation.
2. Promotes graphite flake formation.
3. Increases the fluidity of the molten metal.
4. Improves the ductility of cast iron.
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
Assertion (A): Cast iron is generally hard, brittle and wear resistant.
Reason (R): Cast iron contains more than 2% carbon and as such the percentagecementite in it is higher.
Nodular grey cast iron is obtained from the grey cast iron by adding a smallamount of
Machine tool manufacturers prefer grey cast-iron grade 40 for producing machinecolumns and tables because grey cast-iron is
1. Heavy
2. Easily castable
3. Easily weldable
4. Having good damping capacity
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
Codes:
Consider the following statements:
1. Cast Iron has poor ability to damp vibrations.
2. Cast Iron has higher compressive strength compared to that of steel.
3. Cast Iron parts are suitable where permanent deformation is preferred over fracture.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
|
29 docs|220 tests
|
|
29 docs|220 tests
|

















