Test: Population Interactions - NEET MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test Biology Class 12 - Test: Population Interactions
If the stronger partner is benefitted and the weaker partner is harmed, it is known as
Which type of interaction is being shown in the given figure?

The interdependent evolution of flowering plants and pollinating insects together is known as
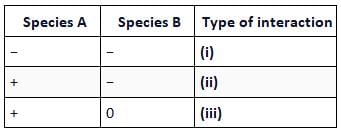
Refer to the given table. If '+' sign has been assigned for beneficial interaction, sign for detrimental interaction and '0' for neutral interaction, identify the type of interaction (i), (ii) and (iii) and select the correct option.
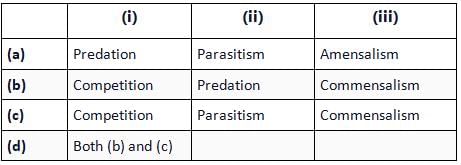
Read the following statements and select the correct option.
Statement 1: Brood parasitism in birds is an example of parasitism in which the parasitic bird lays its eggs in the nest of its host and the host incubates them.
Statement 2: During the course of evolution, the eggs of the parasite bird have evolved to resemble the host's eggs in size and colour to reduce the chances of the host bird detecting the foreign eggs and removing them from the nest.
Refer to the given table that summarises the interactions between two organisms (organisms 1 and organism 2). Identify the types of interaction (A,B and C) and select the correct answer.
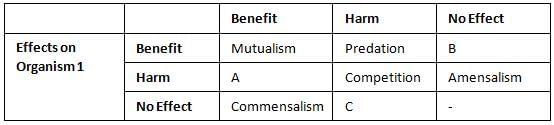
(i) A can be either predation or parasitism
(ii) B can be either commensalism
(iii) C can be amensalism.
(iv) A can be amensalism,
When one population is harmed and the other remains unaffected, the relationship is called
Small fish get stuck near the bottom of a shark and derive their nutrition from it? This kind of association is called
Match the following species with their role in ecological interactions:

Which of the following adaptations are examples of plant defenses against herbivores?
|
78 videos|280 docs|174 tests
|















