Test: Pre-Fertilization (Structures & Events) - NEET MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Pre-Fertilization (Structures & Events)
Which of the following statements regarding the structure of microsporangium are correct?
(i) Microsporangium is generally surrounded by four wall layers-epidermis, endothecium, middle layers, and tapetum.
(ii) Outer three layers perform functions of protection and dehiscence of anthers.
(iii) Cells of tapetum undergo meiosis and produce microspore tetrads.
(i) Microsporangium is generally surrounded by four wall layers-epidermis, endothecium, middle layers, and tapetum.
(ii) Outer three layers perform functions of protection and dehiscence of anthers.
(iii) Cells of tapetum undergo meiosis and produce microspore tetrads.
Read the given statements.
(i) Outer exine is made up of sporopollenin.
(ii) Inner intine is pecto-cellulosic in nature.
(iii) Generative cell is bigger and contains abundant food reserve.
(iv) Vegetative cell is small and floats in the cytoplasm of the generative cell.
Which of the given statements are not true regarding structure of pollen grain?
(i) Outer exine is made up of sporopollenin.
(ii) Inner intine is pecto-cellulosic in nature.
(iii) Generative cell is bigger and contains abundant food reserve.
(iv) Vegetative cell is small and floats in the cytoplasm of the generative cell.
Which of the given statements are not true regarding structure of pollen grain?
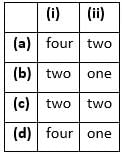
A dithecous anther consists of ____(i)_______microsporangia, _____(ii)_______ in each lobe.
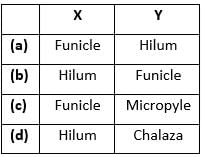
A typical angiospermous ovule is attached to the placenta by means of a stalk called X. Body of the ovule fuses with X in the region called Y. Identify X and Y.
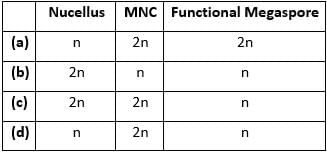
Select the correct option regarding the ploidy level of different structures of an angiospermous ovule.
Which of the following options is correct?
Refer to the given characteristics of some flowers.
(i) Light and non-sticky pollen grains
(ii) Exserted stigmas and anthers
(iii) Large, often feathery stigmas
(iv) Flowers colourless, odourless and nectarless
(v) Common in grasses
Above features are the characteristics of
In (i) condition, both male and female flowers are borne on the same plant; an example of such plants is (ii).
______ of the pollen grain divides to form two male gametes.
One of the major contributors to pollen allergy is ____
What is the function of filiform apparatus in an angiosperm embryo sac?
The part of gynoecium that determines the compatible nature of pollen is?
The three cells found in a pollen grain when it is shed at 3-celled stage are
How many pollen mother cells should undergo meiotic division to produce 64 pollen grains?
The inner most wall layer of anther is tapetum, the main function of tapetum is
One of the most resistant biological material present in the exine of pollen grain is
Which function of tapetum is correct?
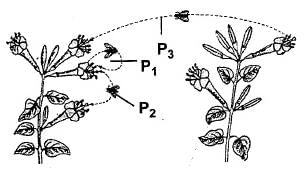
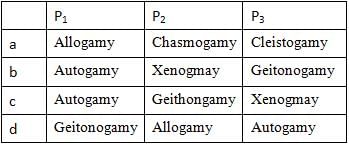
The given diagram shows two plants of the same species. Identify the types of pollination indicated at P1, P2 and P3
.
How many meiotic divisions are required for the formation of 100 pollen grains?
How many meiotic divisions are necessary for formation of 100 functional megaspores.
During the process of fertilization the pollen tube of the pollen grain usually enters the embryo sac through
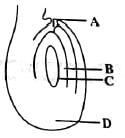
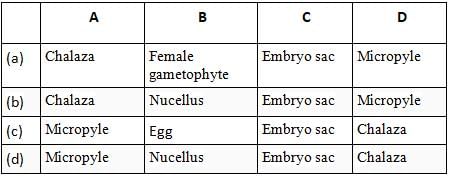
Identify the parts labelled A, B, C and D in the given figure and select the correct option.
In which condition should the ovaries be free?



















