Test: Preparation of Alkyl Halides - NEET MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Preparation of Alkyl Halides
The yield of alkyl bromide obtained as a result of heating the dry silver salt of carboxylic acid with bromine in CCI4 is
Which is incorrect about Hunsdiecker's reaction?
Racemic mixture is obtained due to the halogenation of
The reaction of SOCI2 on alkanols to form alkyl chlorides gives good yields because
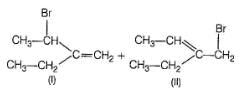
Addition of bromine on propene in the presence of brine yields a mixture of
One or More than One Options Correct Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 8-12) This section contains 5 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE are correct.
Q. Which of the following reagents can bring about free radical chlorination of propane?
What is the order of SN2 reaction of the alkyl halide?
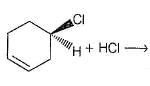
Consider the following reaction,
Q.
The expected product(s) is/are
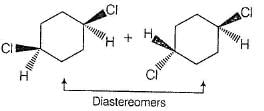
Consider the following reaction,
Q.
When a pure enantiomer of X is taken in the above reaction, correct completion regarding the reaction is/are
Choose the correct statement(s) from the following regarding free radical chlorination and bromination reaction of alkane.
Comprehension Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 13-15) This section contains a paragraph, describing theory, experiments, data, etc.
Three questions related to the paragraph have been given. Each question has only one correct answer among the four given options (a), (b), (c) and (d).
Passage
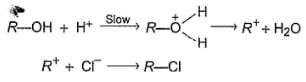
An alcohol (R — OH) can be converted into alkyl chloride by the treatm ent with HCI. Reaction involves protonation of alcohol followed by the formation of carbocation intermediate. Carbocation intermediate in the final step undergo nucleophilic attack by Cl- ion as :
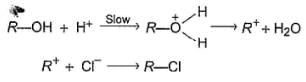
Q.
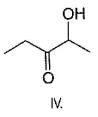
Which of the following alcohols reacts most easily?
An alcohol (R — OH) can be converted into alkyl chloride by the treatm ent with HCI. Reaction involves protonation of alcohol followed by the formation of carbocation intermediate. Carbocation intermediate in the final step undergo nucleophilic attack by Cl- ion as :
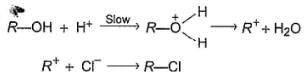
Q.
Which of the following can catalyse the above reaction?
An alcohol (R — OH) can be converted into alkyl chloride by the treatm ent with HCI. Reaction involves protonation of alcohol followed by the formation of carbocation intermediate. Carbocation intermediate in the final step undergo nucleophilic attack by Cl- ion as :
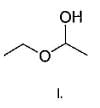
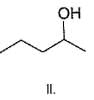
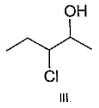
Q.
What is the correct order of reactivty of the followings with HCl?
One Integer Value Correct Type
Direction (Q, Nos. 16-19) This section contains 4 questions. When worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive).
Q.
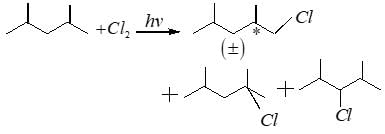
If 2,4-dimethyl pentane is subjected to free radical chlorination reaction, how many different monochlorinated products would be formed?
On free radical chlorination reaction of butane, how many different, optically active, dichloroalkanes would be formed ?
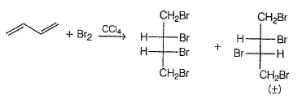
If 1, 3-butadiene is treated with excess of bromine in CCI4 , how many different tetrabromides would be formed?
Consider the following reaction,
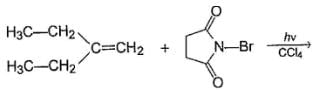
Q.
How many different monobromo derivatives would be produced?
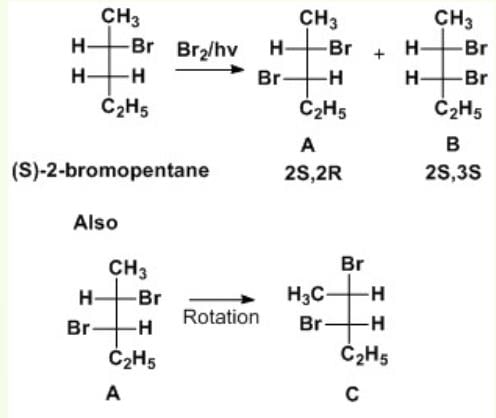
When (S)-2-bromopentane is brominated, several 2, 3-dibromopentane molecules are formed. Which of the following is not formed?
What is the catalyst in the reaction of a primary alcohol with HCl to obtain a chloroalkane?