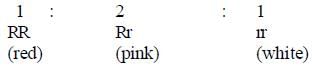Test: Principles of Inheritance and Variation - NEET MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Principles of Inheritance and Variation
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion is followed by a statement of reason. Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion : Mendel was successful in his hybridization.
Reason : Garden pea proved ideal experimental material.
Reason : Garden pea proved ideal experimental material.
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion is followed by a statement of reason. Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion: Mendel used true-breeding pea lines for artificial pollination experiments for his genetic studies.
Reason: For several generations, a true-breeding line shows the stable trait inheritance and expression.
Reason: For several generations, a true-breeding line shows the stable trait inheritance and expression.
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion is followed by a statement of reason. Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion: On true breeding lines, Mendel conducted cross pollination experiments.
Reason: For several generations, true breed line have stable trait inheritance.
Reason: For several generations, true breed line have stable trait inheritance.
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion is followed by a statement of reason. Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion : Cross of F1 individual with recessive homozygous parent is test cross.
Reason : No recessive individual are obtained in the monohybrid test cross progeny.
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion is followed by a statement of reason. Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion: The progeny produced have both the characters of parents.
Reason: The process by which characters pass from parent to progeny is known as inheritance.
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion is followed by a statement of reason. Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion: The progeny in F2-generation traits were identical to their parental type.
Reason: The progeny show no blending of traits.
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion is followed by a statement of reason. Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion: Genes pass from one generation to another.
Reason: The unit of inheritance are genes.
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion is followed by a statement of reason. Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion : In a monohybrid cross, F1 generation indicate dominant characters.
Reason : Dominance occurs only in heterozygous state.
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion is followed by a statement of reason. Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion: In monohybrid cross, at F2 stage, both parental traits are expressed in 3 : 1 proportion.
Reason: At F2 stage, the contrasting parental traits show blending.
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion is followed by a statement of reason. Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion: The cross between the F1 progeny and either of the parent types is a test cross.
Reason: The cross between F1 progeny and the double recessive genotype is back cross.
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion is followed by a statement of reason. Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion : A pair of contrasting characters is termed as allele.
Reason : Only one gene of an allele is expressed in an individual.
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion is followed by a statement of reason. Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion : In Mirabilis, selfing of F1 pink flower plants produces same phenotypic & genotypic ratio.
Reason : Flower colour gene shows incomplete dominance.
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion is followed by a statement of reason. Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion: Gametes receives only one allele of a gene.
Reason: During gamete formation, mitosis takes place leads to formation of haploid cells.
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion is followed by a statement of reason. Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion: In F2 generation of plant Mirabilis jalapa, the pink coloured flowers appear.
Reason: This is observed due epistatic suppression of white colour alleles in one of parental flowers by red colour alleles.
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion is followed by a statement of reason. Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion: A good example of multiple alleles is ABO blood group sytem.
Reason: When IA and IB alleles are present together in ABO blood group sytem, they both express their own types.
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion is followed by a statement of reason. Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion: By means of dihybrid cross, the law of independent assortment can be studied.
Reason: The law of independent assortment is applicable only to linked genes.
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion is followed by a statement of reason. Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion: In Cucurbita pepo, variety of fruit is result of recessive epistasis.
Reason: In recessive epistatsis, a recessive gene at one locus enhances the expression of another gene, at a different locus.
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion is followed by a statement of reason. Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion: The F1-generation resembles boththe parents in codominance.
Reason: An example is different type of red blood cells that determine ABO blood groupingin humans.
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion is followed by a statement of reason. Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion : A women can go to the court if a man refuses to own his child. He has blood group B and women has A while child has O.
Reason : Genetically she is right he can be father of the child.
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion is followed by a statement of reason. Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion: Behaviour of chromosome is parallel to gene.
Reason: Genes are located on the chromosome.