NEET PG Exam > NEET PG Tests > Test: Proteins- 1 - NEET PG MCQ
Test: Proteins- 1 - NEET PG MCQ
Test Description
25 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Proteins- 1
Test: Proteins- 1 for NEET PG 2025 is part of NEET PG preparation. The Test: Proteins- 1 questions and answers have been prepared
according to the NEET PG exam syllabus.The Test: Proteins- 1 MCQs are made for NEET PG 2025 Exam.
Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests for Test: Proteins- 1 below.
Solutions of Test: Proteins- 1 questions in English are available as part of our course for NEET PG & Test: Proteins- 1 solutions in
Hindi for NEET PG course.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET PG Exam by signing up for free. Attempt Test: Proteins- 1 | 25 questions in 25 minutes | Mock test for NEET PG preparation | Free important questions MCQ to study for NEET PG Exam | Download free PDF with solutions
*Multiple options can be correct
Detailed Solution for Test: Proteins- 1 - Question 1
*Multiple options can be correct
Detailed Solution for Test: Proteins- 1 - Question 2
Test: Proteins- 1 - Question 3
Which one of the following can be homologous substitution for isoleucine in a protein in sequence? (AI 2006)
Detailed Solution for Test: Proteins- 1 - Question 3
Test: Proteins- 1 - Question 4
In a mutation if valine is replaced by which of the following would not result in any change in the function of protein: (AIIMS May 02)
Detailed Solution for Test: Proteins- 1 - Question 4
*Multiple options can be correct
Detailed Solution for Test: Proteins- 1 - Question 5
Test: Proteins- 1 - Question 6
Proteins are linear polymers of amino acids. They fold into compact structures. Sometimes, these folded structures associate to form homo-orheterodimers. Which one of the following refers to this associated form? (Al 2006)
Detailed Solution for Test: Proteins- 1 - Question 6
Detailed Solution for Test: Proteins- 1 - Question 7
Detailed Solution for Test: Proteins- 1 - Question 8
Detailed Solution for Test: Proteins- 1 - Question 9
Detailed Solution for Test: Proteins- 1 - Question 10
Detailed Solution for Test: Proteins- 1 - Question 11
Detailed Solution for Test: Proteins- 1 - Question 12
*Multiple options can be correct
Detailed Solution for Test: Proteins- 1 - Question 13
*Multiple options can be correct
Detailed Solution for Test: Proteins- 1 - Question 14
Detailed Solution for Test: Proteins- 1 - Question 15
Detailed Solution for Test: Proteins- 1 - Question 16
*Multiple options can be correct
Test: Proteins- 1 - Question 17
Which of the amino acid is responsible for peptide bond: (PGI Nov 2014)
Detailed Solution for Test: Proteins- 1 - Question 17
Test: Proteins- 1 - Question 18
Which one of the following about protein structure is correct: (PGI May 2015)
Detailed Solution for Test: Proteins- 1 - Question 18
Test: Proteins- 1 - Question 19
An alpha helix of a protein is most likely to be disrupted if a missense mutation introduces the following amino acid within the alpha helical structure: (AIIMS Nov 2002)
Detailed Solution for Test: Proteins- 1 - Question 19
Test: Proteins- 1 - Question 20
Precipitation of proteins occur in all except: (AIIMS Nov 2015)
Detailed Solution for Test: Proteins- 1 - Question 20
Test: Proteins- 1 - Question 21
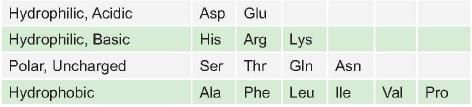
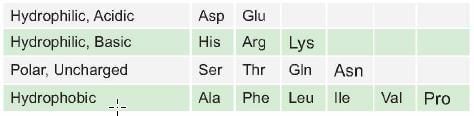
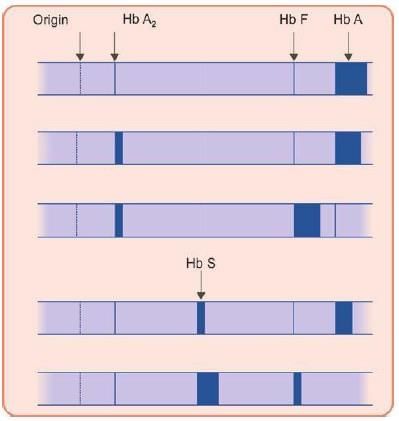
In Hb S, Glutamic acid replaced by valine. What will be its electrophoretic mobility?
Detailed Solution for Test: Proteins- 1 - Question 21
Test: Proteins- 1 - Question 22
Following SDS PAGE electrophoresis, protein is found to be 100 kDa, After treatment with mercaptoethanol, it shows 2 bands of 20 KDa and 30 KDa widely separated. True statement is:
Detailed Solution for Test: Proteins- 1 - Question 22
Test: Proteins- 1 - Question 23
Protein is purified using ammonium sulfate by: (AIIMS Nov 2010)
Detailed Solution for Test: Proteins- 1 - Question 23
Test: Proteins- 1 - Question 24
All of the following can determine the protein structure, except: (AIIMS Nov 2008)
Detailed Solution for Test: Proteins- 1 - Question 24
Test: Proteins- 1 - Question 25
Method used to study the structure of proteins include all except:
Detailed Solution for Test: Proteins- 1 - Question 25
Information about Test: Proteins- 1 Page
In this test you can find the Exam questions for Test: Proteins- 1 solved & explained in the simplest way possible.
Besides giving Questions and answers for Test: Proteins- 1, EduRev gives you an ample number of Online tests for practice
Download as PDF