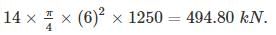Test: RCC Design- 4 - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test GATE Civil Engineering (CE) 2026 Mock Test Series - Test: RCC Design- 4
Which of the following losses of prestress occurs only in pre-tensioning and not in post-tensioning?
As per IS 1343, The minimum clear spacing in case of single wires used in pre-tensioning system shall not be less than:
In accordance with IS 1343: 1980, in the absence of data, the approximate value of shrinkage strain for the design of post-tensioning concrete member if the age of concrete at transfer is 3 days will be?
Match List – I (Post-tensioning system) with List – II (Arrangement of tendons in the duct) and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:
List - I
A. Freyssinte
B. Gifford-Udall
C. Lee-McCall
D. Magnel-Blaton
List – II
1. Single bars
2. Wires evenly spaced by perforated spacers
3. Horizontal rows of four wires spaced by metal grills
4. Wires spaced by helical wire core in annular spacer
An ordinary mild steel bar has been prestressed to working stress of 200 MPa. Young’s modulus of steel is 200 GPa. Permanent negative strain due to shrinkage and creep is 0.0008. How much is the effective stress left in steel?
The percentage loss of prestress due to anchorage slip of 0.3 mm in a concrete beam of length 30 m which is post-tensioned by a tendon with initial stress of 1200 N/mm2 and modulus of elasticity equal to 2.1 × 105 N/mm2 is:
A prestress concrete rectangular beam of size 300 mm × 900 mm is pre-stressed with an initial prestressing force of 700 kN at an eccentricity of 300 mm. Stress at the top beam section due to prestress alone in, N/mm2 is:
A concrete beam is prestressed by a cable carrying an initial prestress of 500 N/mm2. The percentage loss in prestressing due to shrinkage of concrete if the beam is pre-tensioned and post-tensioned. (Consider the age of concrete at transfer is 8 days, Es = 2 x 105 N/mm2)
A prestressed beam of size 250 × 400 mm deep is prestressed by 14 tendons of 6 mm diameter. The cable is located at 150 mm from the bottom of the beam. If the initial prestress in the beam is 1250 N/mm2. The loss of prestress due to elastic deformation and creep of concrete respectively will be?
Assume:
M-40 Grade concrete
creep coefficient = 1.6
Modulus of elasticity = 2 × 105 MPa.
Neglect the effect due to dead load.
|
33 docs|291 tests
|



 times the maximum size of aggregate.
times the maximum size of aggregate.