Test: Rectangular Solids- 3 - GMAT MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Rectangular Solids- 3
A 5 cubic centimeter cube is painted on all its side. If it is sliced into 1 cubic centimer cubes, how many 1 cubic centimeter cubes will have exactly one of their sides painted?
The area of a square field is 24200 sq m. How long will a lady take to cross the field diagonally at the rate of 6.6 km/hr?
The circumference of the front wheel of a cart is 30 ft long and that of the back wheel is 36 ft long. What is the distance travelled by the cart, when the front wheel has done five more revolutions than the rear wheel?
If the sides of a triangle measure 72, 75 and 21, what is the measure of its in radius?
A 5 cm cube is cut into as many 1 cm cubes as possible. What is the ratio of the surface area of the larger cube to that of the sum of the surface areas of the smaller cubes?
If each interior angle of a regular polygon is 150 degrees, then it is a/an ______________
Four horses are tethered at 4 corners of a square field of side 70 metres so that they can just about reach one another. The area left ungrazed by the horses is:
A square sheet of paper is converted into a cylinder by rolling it along its length. What is the ratio of the base radius to the side of the square?
The surface area of the three coterminous faces of a cuboid are 6, 15, 10 sq.cm respectively. Find the volume of the cuboid.
If the diagonal and the area of a rectangle are 25 m and 168 m2, what is the length of the rectangle?


 a –-- (2)
a –-- (2) meters.
meters. (converting 1 km = 1000 meters and 1 hour = 60 minutes).= 2 minutes
(converting 1 km = 1000 meters and 1 hour = 60 minutes).= 2 minutes
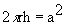
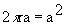
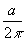 Ratio of base radius to side of square =
Ratio of base radius to side of square = 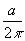 : a =
: a =