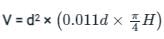Test: Sedimentation Tanks - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Sedimentation Tanks
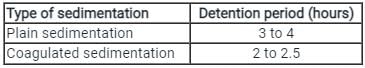
In continuous flow sedimentation tanks the actual detention period used in practice should be
What are the ponds constructed for removing entrained solids called?
The tanks built with mechanical means for continuous removal of solids being deposited by sedimentation are called ____
For a given discharge, the efficiency of sedimentation tank can be increased by :
The design of the sedimentation basins totally depends upon the ______.
What is the accumulated layer at the bottom of the tank called as?
How many types of sedimentation tanks are there based on the method of operation?
How many types of sedimentation tanks are present based on the shape of the tank?
What is the time period for which the water is stored in fill and draw type of sedimentation tank?
For a given discharge, the efficiency of sedimentation tank can be increased by:


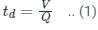 [Valid for both rectangular and circular tanks]
[Valid for both rectangular and circular tanks]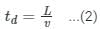 [Valid for rectangular tank only]
[Valid for rectangular tank only]