Test: Sensory Reception & Processing (NCERT) - Grade 9 MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test AP Biology - Test: Sensory Reception & Processing (NCERT)
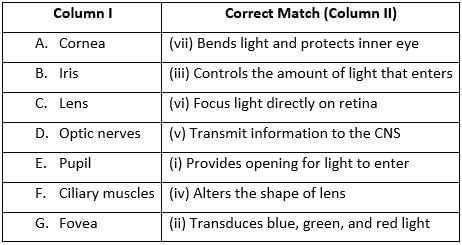
Match column I with column II and select the correct option from the codes given below

The part of the ear where sound is transduced is
The structures in a human body that assist in body balance are located in the
Bony labyrinth is filled with a fluid called
Eustachian tube is a passage connecting the
Which of these structures are present on the retina?
In the chemistry of vision in mammals, the photosensitive substance is called
Cornea transplant in humans is almost never rejected. This is because
The black pigment in the eye, which reduces the internal reflection, is located in
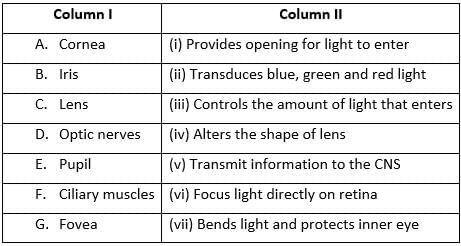
Identify the structure in the given diagram.
Which of the following cells are associated with identification of colours in bright light?
The size of pupil is controlled by the
Cornea is covered externally by a thin transparent membrane which is called
The gelatinous membrane covering the sensory hair cells of the ear is known as
Retina of eye is analogous to which part of camera?
The point in eye of mammals from which optic nerves and blood vessels leave the eye ball is called
The fluid filled in the space between lens and cornea is termed as
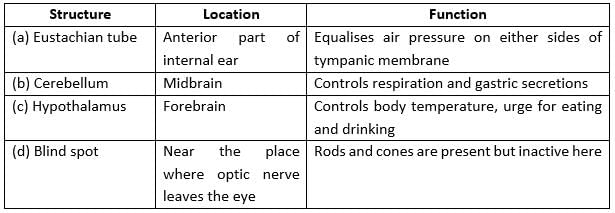
Select the option that correctly matches the structures with its location and function.
The innermost layer of the human eye
|
130 videos|198 docs|114 tests
|