Test: Separations and Purifications - MCAT MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Separations and Purifications
500 mL of water and 500 mL of dichloromethane (d = 1.3 g/mL) are added to a mixture containing benzoic acid, cresol, methoxyethane, and N-methylethanamine. Four solutions are available for extraction of the mixture: HCN, HCl, NaOH, and LiHCO3. After the initial wash, the top layer from each extraction was retained and one of the preceding solutions was added. Which of the following statements most accurately describes this procedure?
On which of the following physical properties does the separation of the constituents of a mixture by column chromatography depend?
An azeotrope is a mixture of liquids whose proportions cannot be changed by simple distillation because, when it is boiled, the vapor has the same proportions of constituents as the unboiled mixture. From an azeotropic mixture of 95% ethanol and 5% water, which of the following methods would NOT allow for further purification of ethanol at the azeotropic point?
What solvent would be most effective at purifying through recrystallization a quantity of sugar contaminated with some table salt?
Which of the following statements most accurately describes thin-layer chromatography?
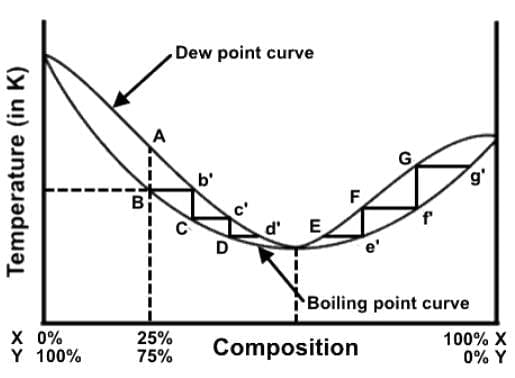
A distillation procedure is performed with a starting mixture of 25% X and 75% Y, and the distillation steps have been superimposed onto the liquid-vapor phase diagram. Which of the following statements best describes this distillation process in relation to the phase diagram?
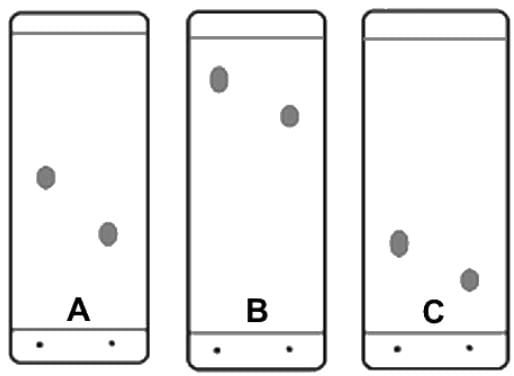
Which of the following additional set of conditions (listed first the adsorbent and second the solvent or eluent) would produce the following TLC plates?
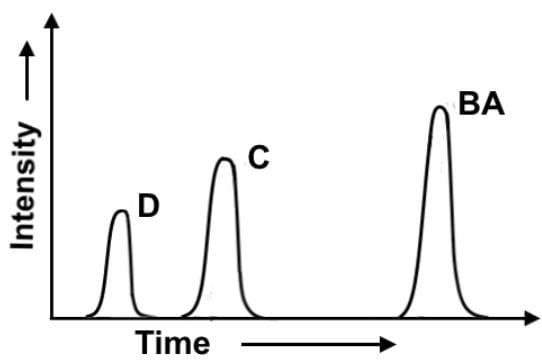
In the chlorination of 2-methylbutane at 300°, all four possible monosubstitution products (compounds A-D) are created. On a purely statistical basis, the ratio of the products (50%:25%:17%:8%) should correlate with the number of available hydrogens at the various positions, 6:3:2:1 respectively. A gas chromatograph separation was performed after the reaction was complete to evaluate the experimental ratios of the 4 products. Which of the following statements most accurately describes the gas chromatogram?
A tetrapeptide Tuffsin has the following amino acid sequence: Thr-Lys-Pro-Arg. Tuftsin binds to specific receptors on the surface of macrophages stimulating their migration and phagocytic activity. Proteins can be separated electrophoretically on the basis of net charge by isoelectric focusing in a pH gradient. At pH = 6, what is the overall charge of the tetrapeptide and the direction of travel in the gel?
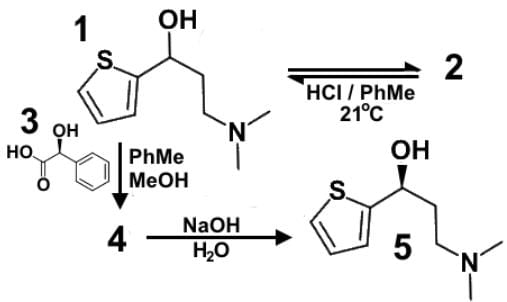
Duloxetine or Cymbalta® (1) is a serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI) prescribed for major depressive disorder, generalized anxiety disorder, fibromyalgia and neuropathic pain. A racemic mixture of Duloxetine (2) is dissolved in a mixture of toluene and methanol to which solution is also added optically active mandelic acid (3). Sodium hydroxide is added to obtain the final product (5). Which of the following statements most accurately describes the role of the various compounds?