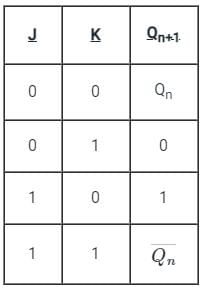
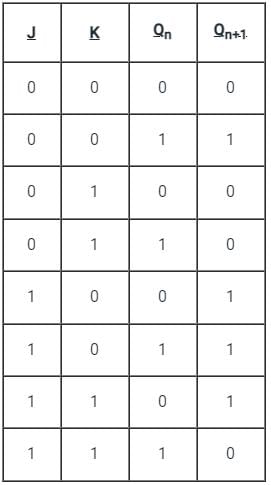
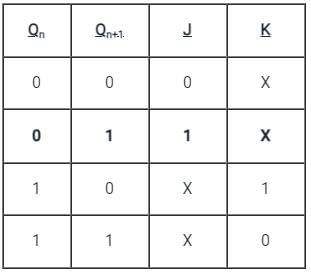
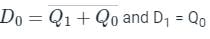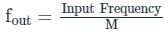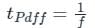Test: Sequential Circuit - Electrical Engineering (EE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Sequential Circuit
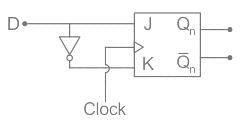
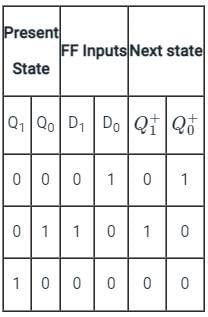
For the circuit shown, the counter state (Q1Q0) follows the sequence
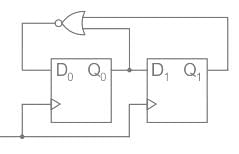

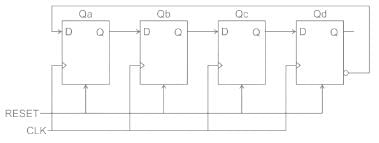
A shift register with its complement output (Q’) of the last stage connected to the D-input of the first stage is called:
A pulse train with a frequency of 1 MHz is counted using a mod-1024 ripple counter built with J-K flip-flops. For proper operation of the counter the maximum permissible propagation delay per flip-flop stage is
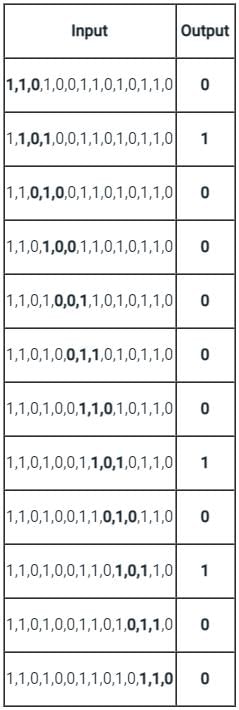
A sequence detector is designed to detect precisely 3 digital inputs, with overlapping sequences detectable. For the sequence (1,0,1) and input data (1,1,0,1,0,0,1,1,0,1,0,1,1,0), what is the output of this detector?
Comprehension:
Read the following paragraph and answer the questions.
A digital counter is a set of flipflops whose states change in response to the pulses applied at Input. Counters can be asynchronous counters or synchronous counters. A counter is an example of a state machine; the number of states is called the modulus. Two basic types of state machines are the Moore and the Mealy. In Moore machine, the combinational logic is a gate array with outputs that determine the next state of the flip-flops in the memory. For Mealy machine, the present state affects just as in Moore machine but in addition, the inputs also affect the outputs.
In a 4-bit asynchronous binary counter, each D flip-flop is negative edge-triggered and has a propagation delay for 10 nanoseconds. What is the highest frequency allowed for the counter to avoid problems due to propagation delay?
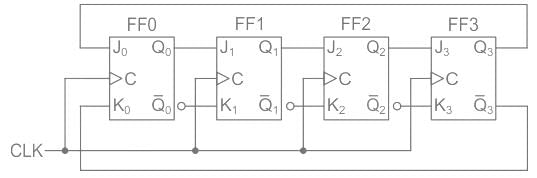
The number of flip-flops required for constructing a mod-12 counter is:
Three T flip flops are connected to form a counter. The maximum states possible for the counter will be:
An eight-bit binary ripple UP counter with a modulus of 256 is holding the count 01111111. What will be the count after 135 clock pulses?