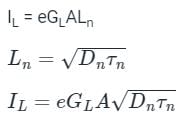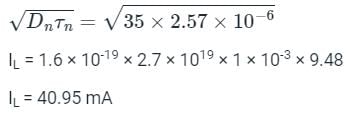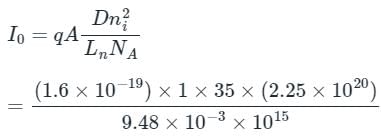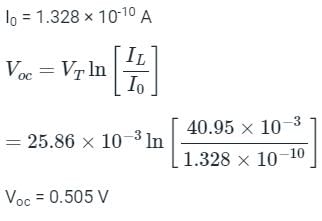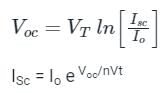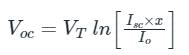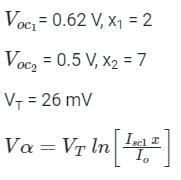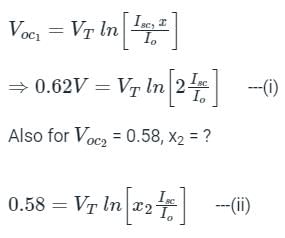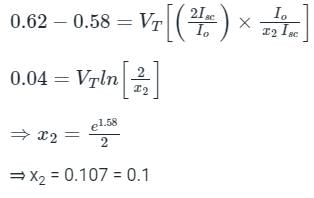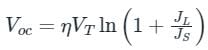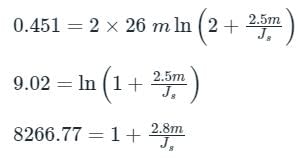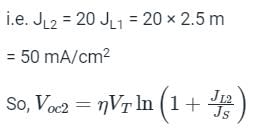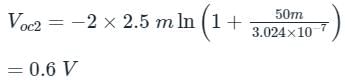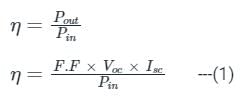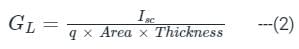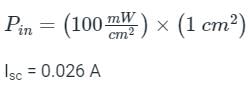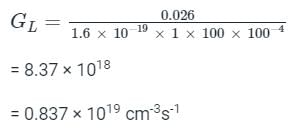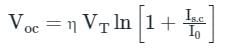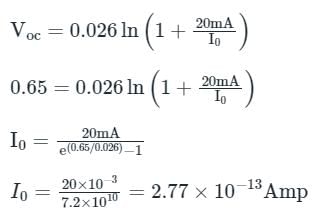Test: Solar Cell - Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Solar Cell
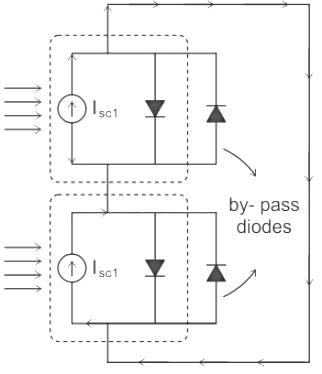
What is the purpose of using bypass diodes in the series connected solar panels?
Consider a silicon n+p junction solar cell with a 1 cm2 surface area and NA = 1015/cm3. Calculate IL (light current) and Voc (open circuit voltage).
Assume Dn = 35cm2sec-1, τn = 2.57 μsec and GL = 2.7 × 1019 cm3 sec-1, VT = 25.86 x 10-3 V, ni = 1.5 x 1010 cm3.
A solar cell have open circuit voltage of 0.62 V for sun intensity of 2. (Assume Vτ = 26 mV). For open circuit voltage of 0.58 V, the value of sun intensity is x. Then, x =
For a particular intensity of incident light on a silicon p-n junction solar cell, the photocurrent density (JL) is 2.5 mA/cm2 and the open-circuit voltage (Voc) is 0.451 V. Consider thermal voltage (VT) to be 25 mV. If the intensity of the incident light is increased by 20 times, assuming that the temperature remains unchanged, Voc (in volts) will be ___________.
(Take the ideality factor, η = 2 for Silicon)
A pn junction solar cell of area 1.0 cm2, illuminated uniformly with 100 mW cm-2, has the following parameters: Efficiency = 15%, open circuit voltage = 0.7 V, fill factor = 0.8, and thickness = 200 μm. The charge of an electron is 1.6 × 10-19 C. The average optical generation rate (in cm-3s-1) is
A solar cell of area 1.0 cm2, operating at 1.0 sun intensity, has a short circuit current of 20 mA, and an open circuit voltage of 0.65 V. Assuming room temperature operation and thermal equivalent voltage of 26 mV, the open circuit voltage (in volts, correct to two decimal places) at 0.2 sun intensity is ________.