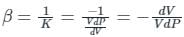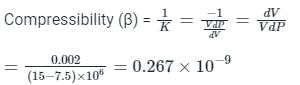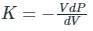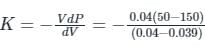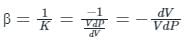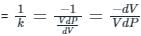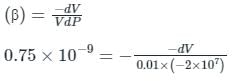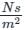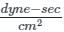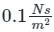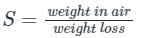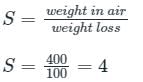Test: Specific Weight & Specific Gravity - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test Fluid Mechanics for Civil Engineering - Test: Specific Weight & Specific Gravity
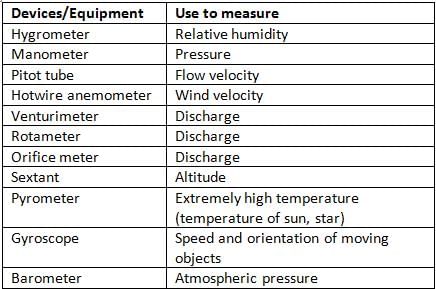
Which of the following instrument is used to measure the specific gravity of liquid ?
Hydrometer is an instrument for measuring
An increase in pressure of a liquid from 7.5 MPa to 15 MPa results into 0.2 percent decrease in its volume. The coefficient of compressibility of the liquid in m2/N is
A liquid compressed in cylinder has a volume of 0.04 m3 at 50 kg/cm2 and a volume of 0.039 m3 at 150 kg/cm2. The bulk modulus of liquid is
A reservoir of capacity 0.01 m3 is completely filled with a fluid of coefficient of compressibility 0.75 × 10-9 m2/N. The amount of fluid that will spill over (in m3), if pressure in the reservoir is reduced by 2 × 107 N/m2 is
The volume of a fluid occupied by a unit mass of the fluid is called -
Specific gravity of marble stone which weighs 400 N in air and 300 N in water is ________
|
54 videos|97 docs|110 tests
|