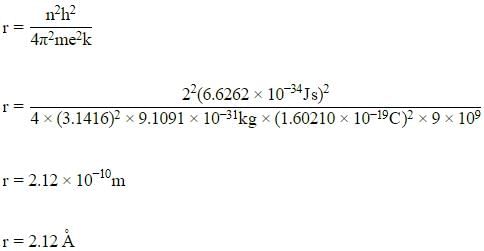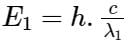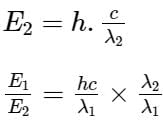Test: Structure of Atom - 1 - NEET MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Structure of Atom - 1
If the kinetic energy of an electron is increased four times, the wavelength of the de-Broglie wave associated with it would become
Calculate the wavelength (in nanometer) associated with a proton moving at 1.0×103ms-1 (Mass of proton = 1.67×10-27kg and h = 6.63×10-34Js)
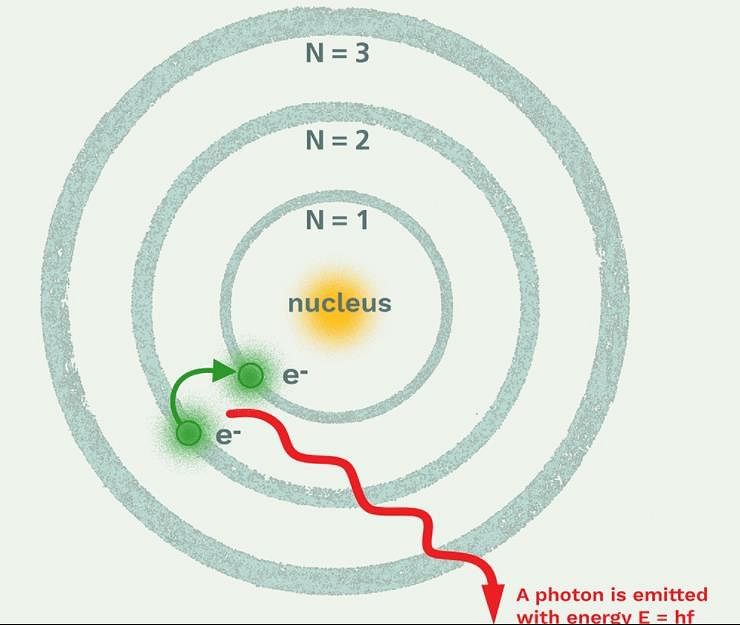
The frequency of light emitted for the transition n = 4 to n = 2 of He+ is equal to the transition in H atom corresponding to which of the following
The maximum number of atomic orbitals associated with a principal quantum number 5 is
The radius of the second Bohr orbit for the hydrogen atom is :
(Planck’s constant, h = 6.262×10-34Js: Mass of electron = 9.1091×10-31kg; Charge of electron e = 1.60210×10-19C; permittivity of vacuum ε0 = 8.854185×10-12kg-1m-3A2)
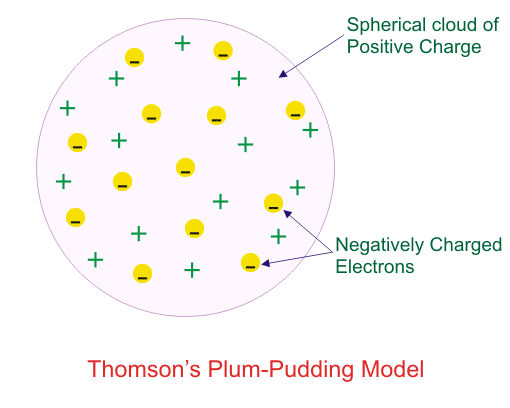
Which model describes that there is no change in the energy of electrons as long as they keep revolving in the same energy level and atoms remains stable?
A sub-shell with n = 6 , l = 2 can accommodate a maximum of
Which of the following conclusions could not be derived from Rutherford’s α -particle scattering experiment?
The wavelengths of two photons are 2000 Å and 4000 Å respectively. What is the ratio of their energies?