Test: Thermodynamics (August 18) - NEET MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test Daily Test for NEET Preparation - Test: Thermodynamics (August 18)
What is the entropy change (in JK–1 mol–1) when one mole of ice is converted into water at 0º C? (The enthalpy change for the conversion of ice to liquid water is 6.0 kJ mol–1 at 0ºC) [2003]
For which one of the following equations is ΔHºreact equal to ΔHfº for the product? [2003]
If the bond energies of H-H, Br-Br, and HBr are 433, 192 and 364 kJ mol–1 respectively, the ΔH° for the reaction H2(g) + Br2(g) → 2HBr(g) is: [2004]
The work done during the expansion of a gas from a volume of 4 dm3 to 6 dm3 against a constant external pressure of 3 atm is: (1L atm = 101.32 J) [2004]
The absolute enthalpy of neutralisation of the reaction: MgO (s) + 2HCl (aq) —→ MgCl2(aq) + H2O (l) will be:[2005]
Which of the following pairs of a chemical reaction is certain to result in a spontaneous reaction? [2005]
The enthalpy and entropy change for the reaction Br2(l) + Cl2(g) → 2BrCl(g) are 30kJ mol–1 and 105 JK–1 mol–1 respectively.The temperature at which the reaction will be in equilibrium is: [2006]
Assume each reaction is carried out in an open container. For which reaction will ΔH = ΔE? [2006]
Given that bond energy of H–H and Cl–Cl is 430 kJ mol–1 and 240 kJ mol–1 respectively and ΔHf for HCl is - 90 kJ mol–1, bond enthalpy of HCl is: [2007]
Which of the following are not state functions? [2008]
(I) q + w
(II) q
(III) w
(IV) H - TS
Bond dissociation enthalpy of H2, Cl2, and HCl are 434, 242, and 431 kJ mol–1 respectively. Enthalpy of formation of HCl is: [2008]
From the following bond energies: [2009]
H – H bond energy: 431.37 kJ mol–1
C = C bond energy: 606.10 kJ mol–1
C – C bond energy: 336.49 kJ mol–1
C – H bond energy: 410.50 kJ mol–1
Enthalpy for the reaction, will be:
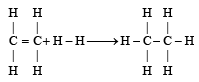
For vapor ization of water at 1 atmospheric pressure, the values of ΔH and ΔS are 40.63 kJmol–1 and 108.8 JK–1 mol–1, respectively. The temperature when Gibbs energy change (ΔG) for this transformation will be zero, is: [2010]
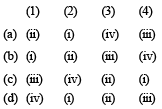
Match List -I (Equations) with List-II (Type of processes) and select the correct option. [2010]

Options:
|
12 docs|366 tests
|


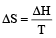
 = 21.98 JK -1mol-1
= 21.98 JK -1mol-1
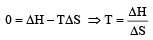
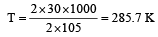
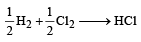
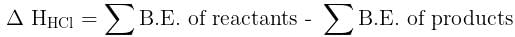
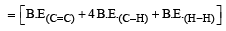
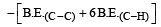
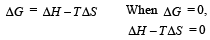
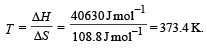
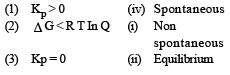
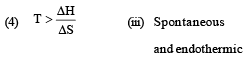
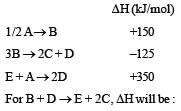 [2011M]
[2011M]

















