Test: Viral Hepatitis- 2 - NEET PG MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Viral Hepatitis- 2
The commonest hepatotropic virus causing increased chronic carrier state is: (Recent Pattern 2014-15)
True about hepatitis with HCV is; (Recent Pattern 2014-15)
A 35-year-old male patient presented with history of jaundice for 15 days. The onset was preceded by a prodromal illness. His serum tested positive for HbsAg. A clinical diagnosis of acute hepatitis B was made. What should be the next best confirmatory investigation? (Recent Pattern 2014-15)
A 45 day old infant developed icterus and two days later symptoms and signs of acute liver failure appeared. Child was found to be positive for HbsAg. The mother was also HbsAg carrier. The mother's hepatitis B serological profile is likely to be: (Recent Pattern 2014-15)
Vertical transmission of hepatitis C is: (Recent Pattern 2014-15)
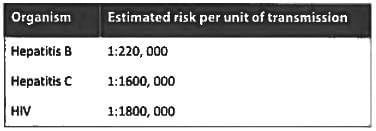
The most common type of hepatitis associated with blood transfusion: (Recent Pattern 2014-15)
Antigen which does not appear in blood in hepatitis B: (Recent Pattern 2014-15)
The most common presentation of hepatitis A is: (Recent Pattern 2014-15)
Granulomatosis hepatitis is not caused by: (Recent Pattern 2014-15)
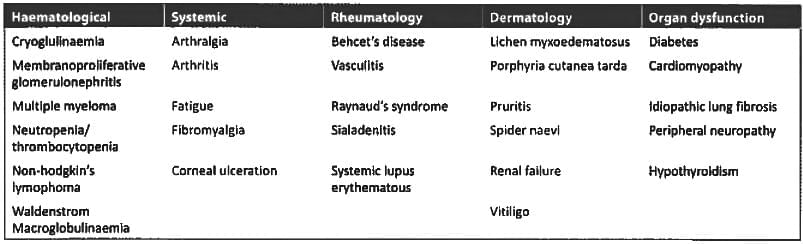
Extrahepatic manifestations of HCV are all except: (PGI Nov 2014)
The commonest hepatotropic virus progressing to chronicity is: (AIIMS May 01)