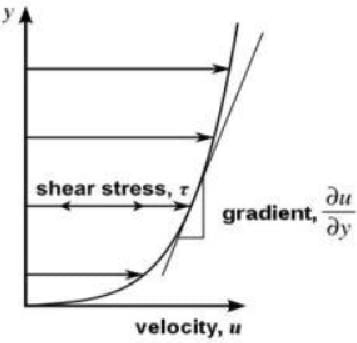
Test: Viscosity - 1 - Mechanical Engineering MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test Fluid Mechanics for Mechanical Engineering - Test: Viscosity - 1
Water flows between two plates of which the upper one is stationary and the lower one is moving with a velocity V. What will be the velocity of the fluid in contact with the upper plate?
The viscous force ____ the relative motion between the adjacent layers of a fluid in motion.Which one of the flowing fits best in the sentence?
The viscosity of a fluid in motion is 1 Poise. What will be it’s viscosity (in Poise) when the fluid is at rest?
Which of the following correctly states how the viscosities of a liquid and a gas will change with temperature?
Which one of the following is not a unit of dynamic viscosity?
Which one of the following is the CGS unit of dynamic viscosity?
The dynamic viscosity of a fluid is 1 Poise. What should one multiply to it to get the answer in N-s/m2?
Which of the following is the dimension of kinematic viscosity?
|
56 videos|154 docs|75 tests
|