UGC NET Paper 2 Sociology Mock Test - 1 - UGC NET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test UGC NET Mock Test Series - UGC NET Paper 2 Sociology Mock Test - 1
The following are the features, Identify the correct set of features of the little community as stated by R. Red-field :
i. Homogeneity
ii. Heterogeneity
iii. Self-sufficiency
iv. Distinctiveness
v. Primary relations
Select the correct answer from the given codes :
The concept of ‘doubling time’ pertains to the study of?
Which one of the following is not strictly a function of social institution?
In the Industrialised Western societies, 12 chief aim of marriage is not only procreation but:
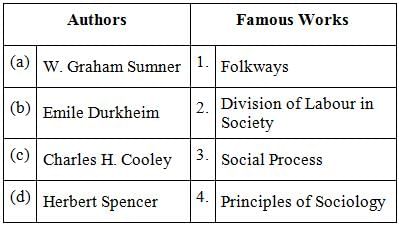
Match the following Authors and their famous works

Direction: In the questions given below are two statements labeled Assertion(A) and Reason(R). In the context of the two statements, which one of the following is correct?
Assertion(A) Functionalism considers human society as a social system, as a set of interconnected parts which together form as a whole.
Reason(R) Social institutions such as education and religion are viewed as a part of the social system rather than as isolated units.
In Action Frame of Reference, Parsons arranged the sub-systems of social action on the basis of
Who is the author of Master of Sociology Thought?
Which of the following concepts Giddens uses in his theory of structuration?
Match List-I with List-II and select the correct answer from the codes given below the lists.

A, B, C, and D are respectively.
When two people interact with each other, they form
Every man in society occupies a number of statuses. Different statuses associated with a single person are known as
Which of the following options are the main tasks of research in modern society?
A crucial difference between interest groups and political parties is that
Which of the following is/are incorrect according to the given passage?
A. A total of about $100 trillion was made by the top 4,000 or so companies in India in 2021–22.
B. Services without factories contribute to ecological decline with their servers and buildings, which decrease global warming.
C. Since the majority of commercial entities are not GST-registered and the country has gone digital, the government have records of what each organisation performs.
According to the passage, net zero carbon emission means?
What can be the suitable title for the passage?
What are the causes of India's severe electricity shortage?
Choose the most appropriate option that describes the meaning of the term ‘renewable energy’ as used in the passage.
Which states were badly affected by the severe power shortage?
Which of the following act is made to prohibit the practice of dowry.
Consider the following regarding De-notified Tribes(DNTs):
1. DNTs stands for all those communities which were once notified under the Criminal Tribes Acts, enforced by the British Raj between 1871 and 1947.
2. The SEED scheme was launched by the Ministry of Tribal Affairs for the welfare of DNTs.
3. More than 10 crore Indians from over 1,400 communities are either denotified, nomadic, or semi-nomadic.
Which of the above is/are correct?
Consider the following statements which is/are correct:
- The Mandal Commission had recommended reservations for the Other Backward Classes in government jobs.
- The Commission is also known as the Socially and Educationally Backward Classes Commission.
|
92 docs|125 tests
|