UGC NET Paper 2 Sociology Mock Test - 5 - UGC NET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test UGC NET Mock Test Series 2025 - UGC NET Paper 2 Sociology Mock Test - 5
Which among the following is not an example of the institution?
Which of the following characterize the Jajmani System?
1. Functional interdependence of castes
2. Mahalwari system
3. Village social structure
Select the correct answer from the codes given below:
Which would a quantitative sociologists use to gather data?
According to Talcott Parsons, traditional values in Asia, Africa and Latin America acted as barriers to development. Which of the following identifies the values enumerated by him?
Given below are two statements:
Assertion(A): The third wave which swept across the world since the 1970s changed the perception of democracy.
Reason(R): This wave of democratisation altered people's perceptions of "democracy" from being a "state of society" that can only be achieved by nations that have historically evolved particular conditions to be an "institution" that was man-made.
Choose the correct option:
1. Law-making is done by leaders only with less participation from people
2. Periodic elections
3. Conflict resolution by government force
4. Equality and Justice
The concept of vicious circle of poverty is related to _____
Which of the following is/are the Aims and Objectives of Labor Welfare?
1. Provide social comfort to employees.
2. Support overall improvement of employees.
3. Provide financial support indirectly to the employees.
4. Contribute in developing sense of responsibility and belongingness among employees.
Find the right code from the given below.
Choose the appropriate answer with regard to Neoliberalism .
1: Neoliberalism challenges the assumption that international anarchy leads to conflict and chaos.
2: Neoliberalism argues for the importance of building a web of international institutions to manage and mitigate global issues.
3: Neoliberalism asserts that states can achieve mutual gains through cooperation and interdependence.
Direction: In the questions below are two statements labelled Assertion (A) and Reason (R). In the context of the two statements which one of the following is correct?
Assertion (A): Labour welfare improves the moral and mental conditions of the workers.
Reason (R): Insurance facility and good working conditions create atmosphere of security and feeling in insecurity is removed.
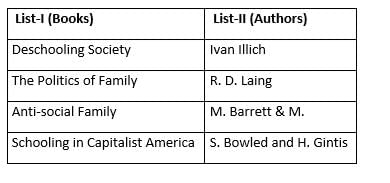
Direction: From the given table select the correct option by matching List-I and List-II.
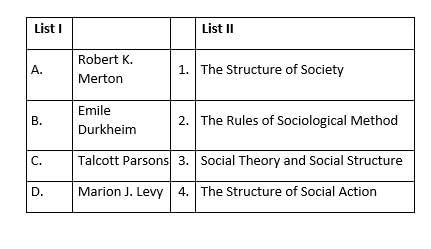
A, B, C, D are respectively.
Which among the following serves as a unifying element in the tribal society?
Which one of the following is not an ascribed status?
Mark out the correct sequence of perspectives on gender and development in India.
Match List-I with List-II.
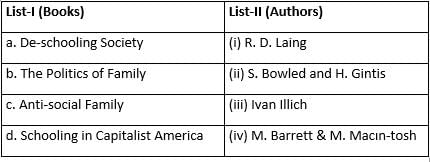
Codes: a, b, c, d
Which of the following represents the correct percentage increase of Carbon dioxide in the atmosphere since pre-industrial times?
Who coined that conflict has functional importance in society?
|
92 docs|125 tests
|