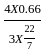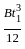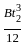UPPSC AE Civil Paper 1 Mock Test - 2 - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test UPPSC AE Civil Mock Test Series 2025 - UPPSC AE Civil Paper 1 Mock Test - 2
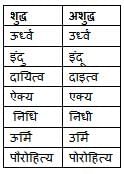
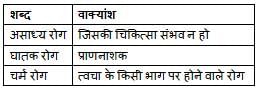
‘हाथी की पीठ पर रखी जाने वाली चौकी ’ वाक्यांश के लिए सार्थक शब्द निम्नलिखित में से है-
वाक्यांशों और उनके लिए प्रयुक्त शब्दों के निम्नलिखित युग्मों में सही युग्म का चयन कीजिए।
अनेकार्थी शब्द 'अक्षर' का इनमें से एक अर्थ नहीं है
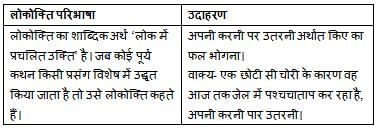
'साझे की हाँड़ी चौराहे फूटी' कहावत का अर्थ है
'वह (व्यक्ति) जिसने संन्यास ग्रहण किया हो' - इस वाक्यांश के लिए एक शब्द है
Which of the following is NOT a quality component?
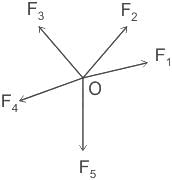
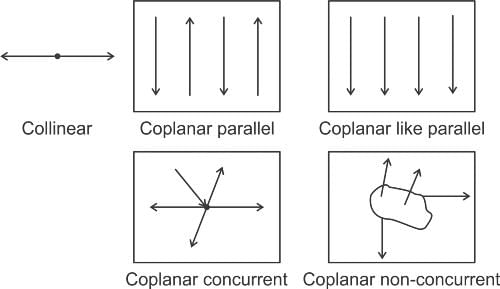
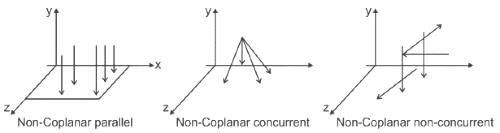
The forces represented in the given figure are called:
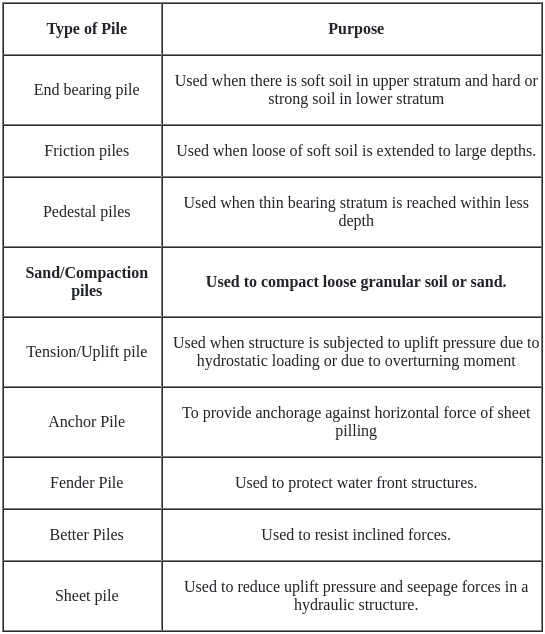
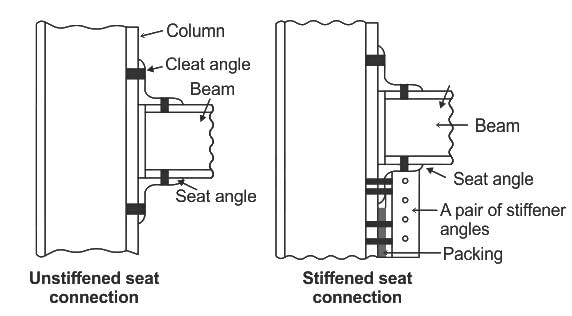
Which of the piles is used for compacting loose granular soil?
A tensile load (P) acts on an axial member of length (l) and cross-sectional area (A) such that it undergoes extensions. If (E) is the elastic modulus the axial stiffness is :
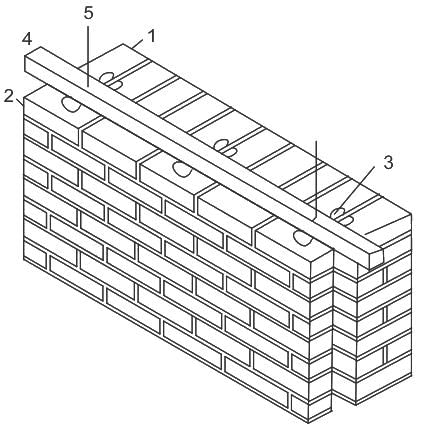
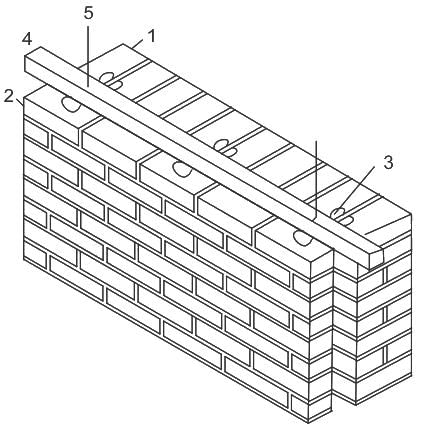
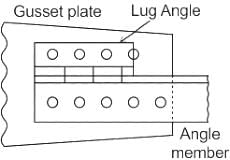
What does item no 3 represents in the above given figure of construction of cavity walls?
Serviceability limit in Limit state method deals with which one of the following?
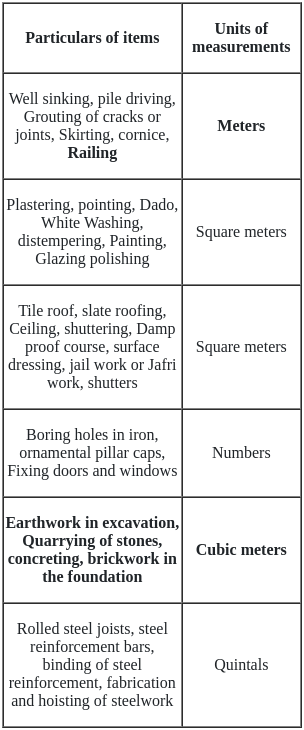
The unit of measurement of pointing in MKS is
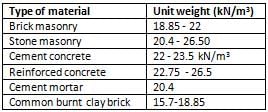
Unit weight of common burnt clay bricks in kN/m3 ranges between
A solid round bar 3 m long and 5 cm in diameter is used as a strut with both ends hinged. If E = 2 × 105 N/mm2 crippling load is
If a particle is moving with simple harmonic motion, the velocity is _________ at the mean position.
The ratio of distance moved by effort to distance moved by load is called
Which of the following statements are correct?
A. Direct cost increases with duration.
B. Direct cost decreases with duration.
C. Indirect cost increases with duration.
D. Indirect cost decreases with duration.
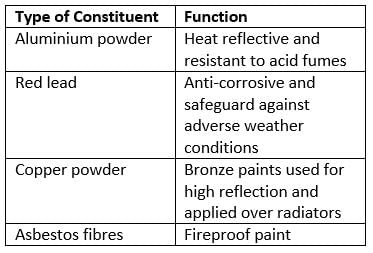
In fireproof paints, the main constituent is:
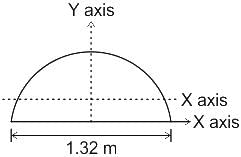
The Y axis of centre of gravity of semicircular plate 1.32 m diameter from its base as shown in figure.
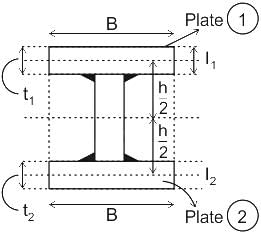
If 'Ib' is moment of inertia of the rolled beam section, 'Ap' is the area of cover plates in one flange and 'h' is the distance between the centroid of the top and bottom flange plates, moment of inertia of built up plate girder is given by





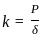
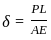
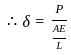
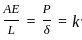
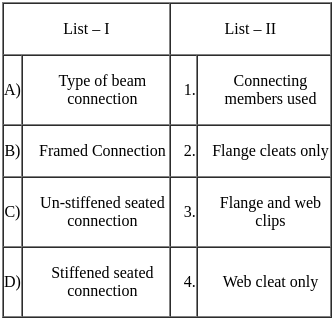
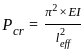
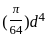 , for the circular column.
, for the circular column.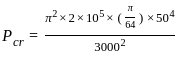
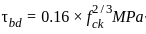
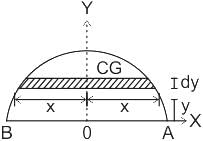
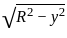
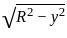 . y . dy
. y . dy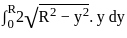
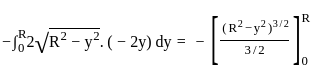
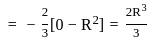 ..........(ii)
..........(ii)