UPPSC GS I Practice Test - 14 (Old Pattern) - UPPSC (UP) MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - UPPSC GS I Practice Test - 14 (Old Pattern)
Consider the following-
1. Article 30 identifies two types of minorities - religious and linguistic.
2. Any educational institution maintained by the state cannot deny admission only on the basis of religion, race, caste, or language.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Consider the following statements:
1. The Constitution does not contain any specific procedure for the selection and appointment of the Prime Minister.
2. The resignation or death of an incumbent Prime Minister automatically dissolves the council of ministers.
Which of the above is/are correct?
Which of the following global conventions was formed to regulate the import and export of hazardous chemicals?
The Ministry of Minority Affairs is organised the 24th “Hunar Haat” in which city?
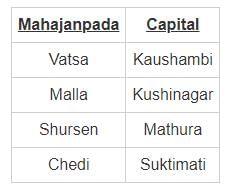
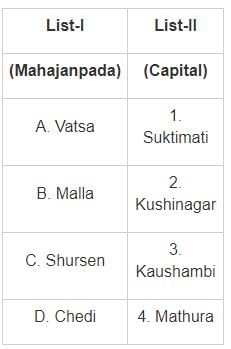
Match the list-I with list-II and select the correct answer using the code given bellow of the list:
Which of the following is a Unitary feature of the government?
Which of the following bird sanctuaries was first established in Uttar Pradesh?
Which pain killer given to cattle is responsible for the near extinction of vultures in India?
Which one of the following symptoms appears in plants because of Manganese deficiency?
Swadeshi movement was the result of the partition of Bengal. Which of the following statements is/are correct concerning the Swadeshi Movement?
1. Bande Mataram became the theme song of this movement.
2. It aimed at boycotting foreign-made goods and adopting Indian goods as an alternative.
3. The Shivaji and Ganpati festivals were organized by Tilak to deliver the Swadeshi message to the masses.
Which of the following words were added to the preamble of the Indian constitution through amendment of the constitution?
1. Socialist
2. Secular
3. Integrity
4. Fraternity
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Which Schedule of the Constitution of India deals with the powers, authority, and responsibilities of Municipalities?
Which among the following countries has not received the vaccines under the 'Vaccine Maitri' programme of the Government of India, as of March 2021?
Which of the following will organize the sixth edition of its annual National Entrepreneurship Summit ‘Start-O-Sphere’ in March 2021?
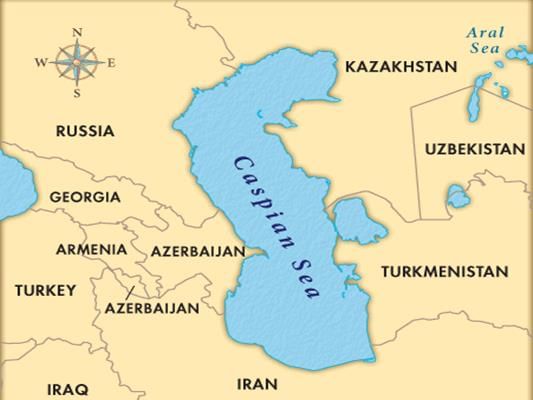
Which among the following does NOT touch the Caspian Sea?
The Government enacted the Panchayat Extension to Scheduled Areas (PESA) Act in 1996. Which one of the following is not identified as its objective?
Which one of the following pairs is correctly matched?

Which of the following pairs is correctly matched?
Who among the following is known as the 'friend, philosopher and guide' of the members of Parliament ?
Given below are two statements, one labelled as Assertion (A) and the other as Reason (R) Assertion (A) : The executive powers of the state are exercised to ensure the compliance of the law of the parliament and the laws applied in the state.
Reason (R) : The government of India can give necessary direction to the states by using its executive powers.
Select the correct answer from the codes given below.
Codes:
Constitution confers executive power of a subject in the Concurrent list to which among the following?
Which of the following forms a part of PM-AASHA ?
1. Price Support Scheme
2. Price Deficiency Payment Scheme
3. Pilot of Private Procurement & Stockist Scheme
Prime Minister Narendra Modi will inaugurate ‘Maitri Setu’ between India and which of the following countries in March 2021?
Which of the following bodies does not/do not find mention in the Constitution?
1. National Development Council
2. Planning Commission
3. Zonal Councils
Select the correct answer using the codes given below.
The source of the Sanskrit phrase 'Satyameva Jayate' lies in the ______.
Consider the following statements regarding the International Solar Alliance.
1. India has been re-elected as the President of the International Solar Alliance (ISA) and Russia as the Co-President for a term of four years.
2. This was the fourth Assembly of the International Solar Alliance.
Which of the following statements given above is/are correct?
In which country is the highest mountain peak of Africa Kilimanjaro located?
'BIMSTEC' is a sub-regional group comprising of seven countries of South Asia and SouthEast Asia headquartered at
Who among the following has written the book titled "Voices of Dissent”?
Which of the following Constitutional Amendment Act made the President bound by the advice of the council of ministers headed by the prime minister?