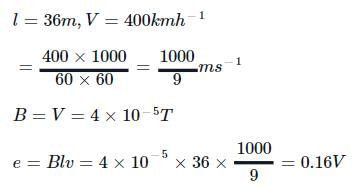VITEEE Physics Test - 4 - JEE MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - VITEEE Physics Test - 4
A device which converts electrical energy into mechanical energy is
According toMoseley's law, the frequency of a spectral line in X - ray spectrum varies as
A cell of e.m.f. E is connected with an external resistance R, then p.d. across cell is V. The internal resistance of cell will be
If sky wave with a frequency of 50 MHz is incident on D-region at an angle of 30o, then angle of refraction is
The resistance of a wire of iron is 10 ohms and temp. coefficient of resistivity is 5x10-3∕℃. At 20oC it carries 30 milliamperes of current. Keeping constant potential difference between its ends, the temperature of the wire is raised to 120oC. The current in milliamperes that flows in the wire is
A wire of resistance 1 Ω is stretched to double its length. The resistance will become
The wing span of an aeroplane is 36 m. If the plane is flying at 400 km/h, the e.m.f. induced between the wings tips is (assume V = 4 X 10-5)
A cylinder of radius R and length L is placed in a uniform electric field E parallel to the cylinder axis, the total electric flux for the surface of the cylinder is
Two charges -10 C and + 10 C are placed 10cm apart. Potential at the centre of the line joining two charges is
What will be the ratio of de Broglie wavelengths of proton and α-particle of same energy
A body of capacity 4 μ F is charged to 80V and another body of capacity 6 μ F is charged to 30V. When they are connected the energy lost by 4 μ F is
A wire of radius r has resistance R. If it is stretched to a radius of 3r/4, its resistance becomes
A capacitor of 10 μF charged up to 250 volts is connected in parallel with another capacitor of 5 μF charged up to 100 volts. The common potential is
Substances which have identical chemical properties but differ in atomic weight are called
The work function of a substance is 4.0 eV. The longest wavelength of light that can cause photoelectron emission from this substance is approximately
A prism of refractive index ' μ ' and angle 'A' is placed in the minimum deviation position. If the angle of minimum deviation is 'A', then the value of 'A' in terms of ' μ ' is
When plate voltage in diode valve is increased from 100 volt to 150 volt then plate current increases from 7.5 mA to 12 mA. The dynamic plate resistance will be
In a good conductor the energy gap between the conduction band and the valence band is
To make P-type semiconductor, the impurity to be mixed with pure germanium will be