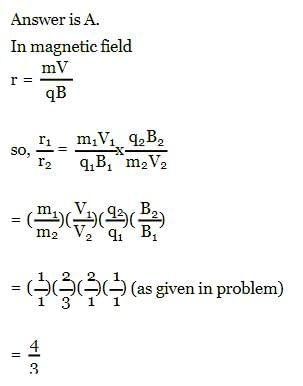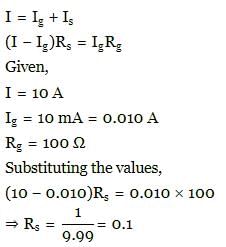VITEEE Physics Test - 9 - JEE MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - VITEEE Physics Test - 9
The value of current, flowing through an inductor of inductance 1 H and having negligible resistance when connected to an a.c. source of 200 V and 50 Hz, is
Two ions having masses in the ratio 1 : 1 and charges 1 : 2 are projected into uniform magnetic field perpendicular to the field with speeds in the ratio 2 : 3. The ratio of the radii of circular paths along which the two particles move is
The negative Zn pole of Daniell cell, sending a constant current through a circuit, decreases in mass by 0.13g in 30 min. If the electrochemical equivalent of Zn and Cu are 32.5 and 31.5 respectively, the increase in the mass of the positive Cu pole in this time is
Two identical cells each of emf E and internal resistance r are connected in parallel with an external resistance R. To get maximum power developed across R, the value of R is
In a potentiometer, the null point is received at 7th wire. If now we have to change the null point at 9th wire, what should we do?
A galvanometer of 100 Ω resistance gives full scale deflection when 10 mA of current is passed. To convert it into 10 A range ammeter, the resistance of the shunt required will be
If two identical heaters of 220 V, 1000 W are placed parallel to each other across 220 V lines, then the combined power of the heaters is
The primary and secondary coils of a transformer have 50 and 1500 turns respectively. If the magnetic flux φ linked with the primary coil is given by φ = φ 0 + 4t, where φ is in weber, t is time in second and φ 0 is a constant, the output voltage across the secondary coil is
A wheel having metal spokes of 1m long between its axle and rim is rotating in a magnetic field of flux density 5x10-5 T normal to the plane of the wheel. An e.m.f of 22/7 mV is produced between the rim and the axle of the wheel. The rate of rotation of the wheel in radians per second is
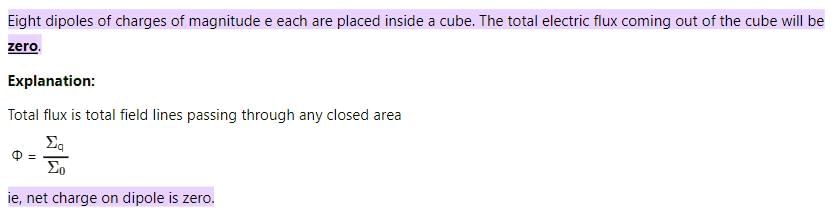
Eight dipoles of charges of magnitude e are placed inside a cube. The total electric flux coming out of the cube will be
A hollow metal sphere of radious 10 cm is charged such that the potential on its surface is 80V. The potential at the centre of the sphere is
In bringing an electron towards another electron, the electrostatic potential energy of the system
The capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor is 10 μF when distance between its plates is 8 cm. If distance between the plates is reduced to 4 cm, its capacitance will be
A solid conducting sphere having a charge Q is surrounded by an uncharged concentric conducting hollow spherical shell. The potential difference between the surfaces of solid sphere and hollow shell is V. If the shell is now given a charge of -3Q, then the new potential difference between the two surfaces will be
A thin spherical conducting shell of radius R has charge q. Another charge Q is placed at the centre of the shell. The electrostatic potential at a point P at a distance R/2 from the centre of the shell is
A straight wire of length 0.5 meter and carrying a current of 1.2 ampere is placed in a uniform magnetic field of induction 2 telsa. The magnetic field is perpendicular to the length of the wire. The force on the wire is
In radioactive decay process, the negatively charged emitted β -particles are
The masses of neutron, proton and deuteron in a.m.u are 1.00893 1.00813 and 2.01473 respectively. The packing fraction of the deuteron in a.m.u is
The energy released per fission of a U235 nucleus is around
A photon of energy 3.4 eV is incident on a metal having work function 2 eV. The maximum K.E. of photo-electrons is equal to
The photoelectric work function for a metal surface is 4.125 eV. The cut off wavelength for this surface is
The refractive index of glass is 1.520 for red light and 1.525 for blue light. Let D1 and D2 be angels of minimum deviation for red and blue light respectively in a prism of this glass, then,
In visible region the dispersive powers and the mean angular deviations for crown and flint glass prisms are ω , ω ' and d, d' respectively. The condition for getting dispersion with zero deviation, when the two prisms are combined is
The valency of an impurity added to germanium crystal in order to convert it into a P-type semi-conductor is
When the P end of P-N junction is connected to the negative terminal of the battery and the N end to the positive terminal of the battery, then the P-N junction behaves like