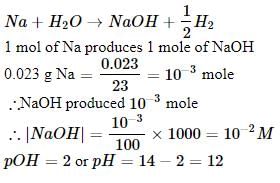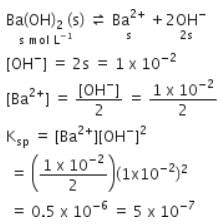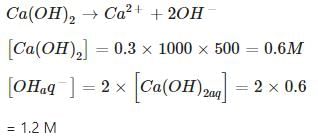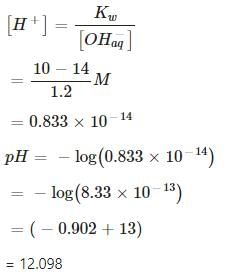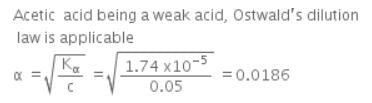P. Bahadur Test: Equilibrium - JEE MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - P. Bahadur Test: Equilibrium
If we place solid iodine in a closed vessel, after sometime the vessel gets filled up with violet vapour. When equilibrium is attained, the intensity of colour will be
A particular ratio of product to reactant helps in predicting the direction in which a given reaction will proceed at any stage. is called
0.023 g of sodium metal is reacted with 100 cm3 of water. The pH of the resulting solution is ______.
BF3does not have proton but still acts as an acid and reacts with NH3. Why is it so? What type of bond is formed between the two?
pH of a solution of a strong acid is 5.0. What will be the pH of the solution obtained after diluting the given solution a 100 times?
The aqueous solution of sugar does not conduct electricity. However, when sodium chloride is added to water, it conducts electricity. How will you explain this statement on the basis of ionisation and how is it affected by concentration of sodium chloride?
pH of a saturated solution of Ba(OH)2 is 12. The value of solubility product (Ksp) of Ba(OH)2 is
0.3 g of Ca(OH)2 is dissolved in water to give 500 mL of solution. The pH of the solution is
The mass of a gas dissolved in a given mass of a solvent at any temperature is proportional to the pressure of the gas above the solvent.
In order to decide what course the reaction adopts and make a qualitative prediction about the effect of a change in conditions on equilibrium we use
Acidity of BF3can be explained on the basis of which of the following concepts?
Calculate the hydrogen ion concentration in the human blood whose pH is 7.38.
Does the number of moles of reaction products increase, decrease or remain same when each of the following equilibria is subjected to a decrease in pressure by increasing the volume?
PCl5(g) 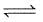 PCl3 (g) + Cl2 (g)
PCl3 (g) + Cl2 (g)
When the soda bottle is opened, some of the dissolved carbon dioxide gas escapes because of
A catalyst increases the rate of the chemical reaction for the conversion of reactants to products by
The dynamic nature of chemical equilibrium can be demonstrated in the synthesis of ammonia by Haber.s process. Choose the appropriate option given below
The ionization constant of acetic acid is 1.74 x 10−5. Calculate the degree of dissociation of acetic acid in its 0.05 M solution. Calculate the concentration of acetate ion in the solution and its pH.
Does the number of moles of reaction products increase, decrease or remain same when each of the following equilibria is subjected to a decrease in pressure by increasing the volume?
PCl5(g) 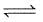 PCl3 (g) + Cl2 (g)
PCl3 (g) + Cl2 (g)
For liquid ⇌vapour equilibrium, at a given temperature, the constant is