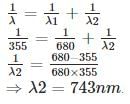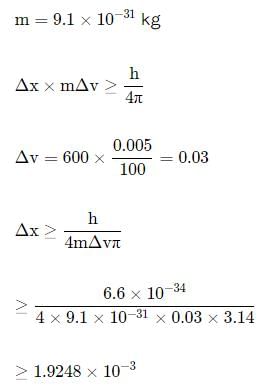Test: Structure of Atom - NEET MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test Chemistry Class 11 - Test: Structure of Atom
Electronic configuration of the element having atomic number 24.
The atom with the given atomic number Z=17, and the atomic mass A=35.5 is
According to quantum mechanics ψ2(r) the wave function squared gives
Spin quantum number with two spin states of the electron represented by two arrows, ↑ (spin up) and ↓ (spin down) was introduced to account for
Values of e/m (charge/mass) in the categories alpha particle (α), electron (e) and protons (p) increase in the order:
A gas absorbs a photon of 355 nm and emits at two wavelengths. If one of the emissions is at 680 nm, the other is at:
The energy associated with the first orbit in the hydrogen atom is -2.18 x 10−18 J/atom. What is the energy associated with the fifth orbit?
Due to the presence of electrons in the inner shells, the electron in the outer shell will not experience the full positive charge of the nucleus (Ze). This is known as
Maximum number of electrons in a subshell with l = 3 and n = 4 is
Arrange the electrons present in the 4d, 3d, 4p and 3p orbitals in order of increasing energies
The Aufbau principle states : In the ground state of the atoms, the orbitals are filled in order of
Radio frequency region of the electromagnetic spectrum is used for broadcasting. It is
In an atom, an electron is moving with a speed of 600m/s with an accuracy of 0.005%. Certainity with which the position of the electron can be located is (h = 6.6 ×10−34 Js)
Give the name and atomic number of the inert gas atom in which the total number of d-electrons is equal to the difference between the numbers of total p and total s electrons.
The ionization energy of the lowest state, also called as the ground state, is:
An cation A3+ has 18 electrons. Write the atomic number of A.
Emission spectrum of a material results from the material's (atom or molecules)
Dalton's atomic theory could not explain one of the following
|
119 videos|338 docs|74 tests
|