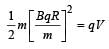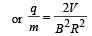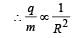31 Year NEET Previous Year Questions: Moving Charges & Magnetism - 1 - NEET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test Physics Class 12 - 31 Year NEET Previous Year Questions: Moving Charges & Magnetism - 1
The magnetic force acting on a charged particleof charge – 2μC in a magnetic field of 2T actingin y direction, when the particle velocity is 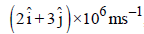 , is
, is
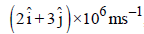 , is
, isUnder the influence of a uniform magnetic field,a charged particle moves with constant speed vin a circle of radius R. The time period of rotationof the particle: [2009]
A thin ring of radius R meter has charge q coulomb uniformly spread on it. The ring rotates about its axis with a constant frequency of f revolutions/s. The value of magnetic induction in Wb/m2 at the centre of the ring is [2010]
A galvanometer has a coil of resistance 100 ohmand gives a full-scale deflection for 30 mAcurrent. It is to work as a voltmeter of 30 voltrange, the resistance required to be added willbe [2010]
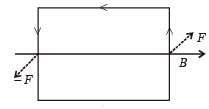
A square current carrying loop is suspended in a uniform magnetic field acting in the plane of the loop. If the force on one arm of the loop is 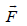 , the net force on the remaining three arms of the loop is
, the net force on the remaining three arms of the loop is
A particle having a mass of 10–2 kg carries a charge of 5 × 10–8 C. The particle is given an initial horozontal velocity of 105 ms–1 in the presence of electric field 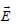 and magnetic field
and magnetic field 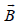 . To keep the particle moving in a horizontal direction, it is necessary that
. To keep the particle moving in a horizontal direction, it is necessary that
(1) 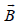 should be perpendicular to the direction of velocity and
should be perpendicular to the direction of velocity and 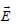 should be along the direction of velocity.
should be along the direction of velocity.
(2) Both 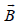 and
and 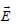 should be along the direction of velocity.
should be along the direction of velocity.
(3) Both 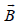 and
and 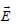 are mutually perpendicular and perpendicular to the direction of velocity.
are mutually perpendicular and perpendicular to the direction of velocity.
(4) 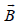 should be along the direction of velocity and
should be along the direction of velocity and 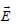 should be perpendicular to the direction of velocity
should be perpendicular to the direction of velocity
Which one of the following pairs of statements is possible?
A closely wound solenoid of 2000 turns and areaof cross-section 1.5 × 10–4 m2 carries a currentof 2.0 A. It suspended through its centre andperpendicular to its length, allowing it to turn ina horizontal plane in a uniform magnetic field 5 ×10–2 tesla making an angle of 30° with the axis ofthe solenoid. The torque on the solenoid will be:
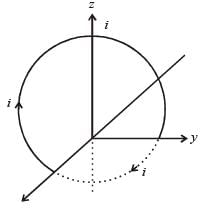
A current loop consists of two identical semicircular parts each of radius R, one lying in the x-y plane and the other in x-z plane. If the current in the loop is i., the resultant magnetic field due to the two semicircular parts at their common centre is
A current carrying loop in the form of a right angle isosceles triangle ABC is placed in a uniform magnetic field acting along AB. If the magnetic force on the arm BC is F, what is the force on the arm AC?
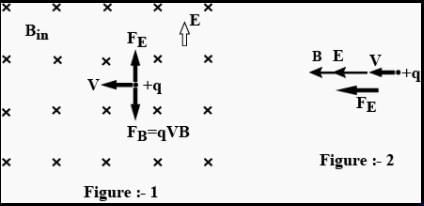
A uniform electric field and uniform magneticfield are acting along the same direction in acertain region. If an electron is projected in theregion such that its velocity is pointed alongthe direction of fields, then the electron [2011]
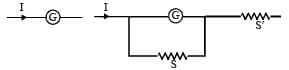
A galvanometer of resistance, G is shunted by a resistance S ohm. To keep the main current in the circuit unchanged, the resistance to be put in series with the galvanometer is [2011M]
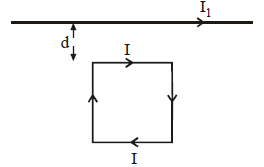
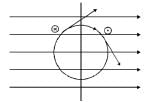
A square loop, carrying a steady current I, is placed in a horizontal plane near a long straight conductor carrying a steady current I1 at a distance d from the conductor as shown in figure. The loop will experience [2011M]
Charge q is uniformly spread on a thin ring of radius R. The ring rotates about its axis with a uniform frequency f Hz. The magnitude of magnetic induction at the centre of the ring is [2011M]
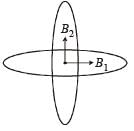
Two similar coils of radius R are lying concentrically with their planes at right angles to each other. The currents flowing in them are
I and 2 I, respectively. The resultant magnetic field induction at the centre will be: [2012]
An alternating electric field, of frequency v, is applied across the dees (radius = R) of a cyclotron that is being used to accelerate
protons (mass = m). The operating magnetic field (B) used in the cyclotron and the kinetic energy (K) of the proton beam, produced by it, are given by : [2012]
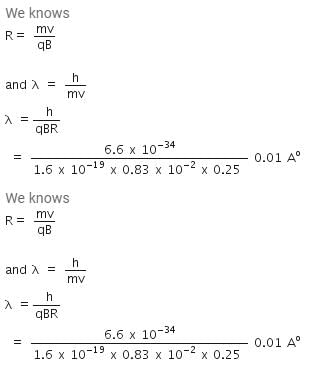
An α-particle moves in a circular path of radius 0.83 cm in the presence of a magnetic field of 0.25 Wb/m2. The de-Broglie wavelengthassociated with the particle will be : [2012]
A proton carrying 1 MeV kinetic energy ismoving in a circular path of radius R in uniformmagnetic field. What should be the energy of an α -particle to describe a circle of same radius inthe same field? [2012M]
A current loop in a magnetic field [NEET 2013]
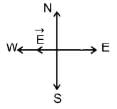
When a proton is released from rest in a room, it starts with an initial acceleration a0 towards west. When it is projected towards north with a speed v0 it moves with an initial acceleration 3a0 towards west. The electric and magnetic fields in the room are respectively [NEET 2013]
A long straight wire carries a certain current and produces a magnetic field of 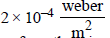 at a perpendicular distance of 5 cm from the wire. An electron situated at 5 cm from the wire moves with a velocity 107 m/s towards the wire along perpendicular to it. The force experienced by the electron will be
at a perpendicular distance of 5 cm from the wire. An electron situated at 5 cm from the wire moves with a velocity 107 m/s towards the wire along perpendicular to it. The force experienced by the electron will be
(charge on electron =1.6 × 10–19 C)
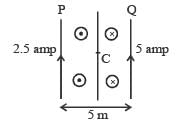
Two long parallel wires P and Q are both perpendicular to the plane of the paper with distance of 5 m between them. If P and Q carry currents of 2.5 amp and 5 amp respectively in the same direction, then the magnetic field at a point half-way between the wires is [2000]
A charged particle of charge q and mass m enters perpendicularly in a magnetic field 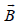 . Kinetic energy of the particle is E; then frequency of rotation is [2001]
. Kinetic energy of the particle is E; then frequency of rotation is [2001]
A charged particle moves through a magneticfield in a direction perpendicular to it. Then the [2003]
A long solenoid carrying a current produces amagnetic field B along its axis. If the current isdouble and the number of turns per cm is halved,the new value of the magnetic field is [2003]
A galvanometer acting as a voltmeter will have [2004]
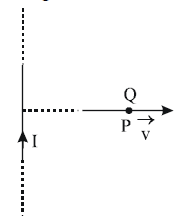
A very long straight wire carries a current I. At the instant when a charge + Q at point P has velocity 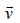 , as shown, the force on the charge is
, as shown, the force on the charge is
When a charged particle moving with velocity 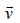 is subjected to a magnetic field of induction
is subjected to a magnetic field of induction 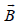 the force on it is non-zero. This implies that
the force on it is non-zero. This implies that
Two circular coils 1 and 2 are made from the samewire but the radius of the 1st coil is twice that ofthe 2nd coil. What potential difference in voltsshould be applied across them so that themagnetic field at their centres is the same [2006]
In a mass spectrometer used for measuring the masses of ions, the ions are initially accelerated by an electric potential V and then made to describe semicircular path of radius R using a magnetic field B. If V and B are kept constant, the ratio 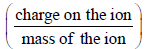 will be proportional to
will be proportional to
A particle of mass m, charge Q and kinetic energyT enters a transverse uniform magnetic field ofinduction 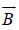 . After 3 seconds, the kinetic energyof the particle will be: [2008]
. After 3 seconds, the kinetic energyof the particle will be: [2008]
|
88 videos|421 docs|88 tests
|


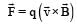
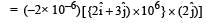
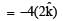
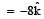
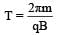

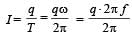

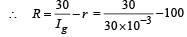
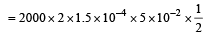
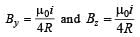
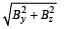
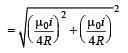

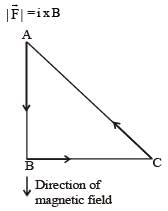
 will be in the direction perpendicular to the plane of the paper and going into it.
will be in the direction perpendicular to the plane of the paper and going into it.
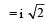 x B sin 45°
x B sin 45°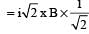
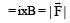
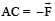
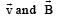 are in same direction so that magnetic force on electron becomes zero, only electric force acts. But force on electron due to electric field is opposite to the direction of velocity.
are in same direction so that magnetic force on electron becomes zero, only electric force acts. But force on electron due to electric field is opposite to the direction of velocity.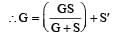
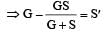
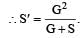
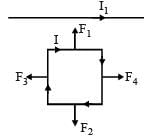
 and F3 and F4 are equal and opposite. Hence, the net attraction force will be towards the conductor.
and F3 and F4 are equal and opposite. Hence, the net attraction force will be towards the conductor.
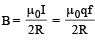
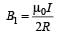
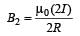
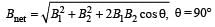
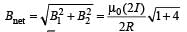
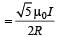
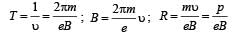
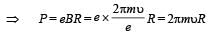
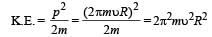
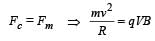
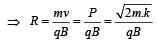
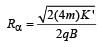
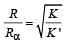
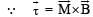 = M B sinθ
= M B sinθ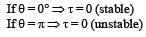
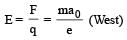
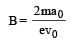 (downward)
(downward)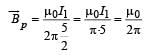
 is downward
is downward 
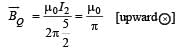
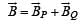
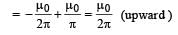
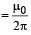
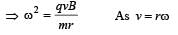
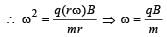
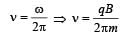
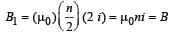
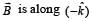
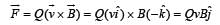
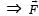 is along OY.
is along OY.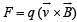
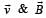 is either zero or 180º, then value of F will be zero as cross product of
is either zero or 180º, then value of F will be zero as cross product of 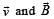 will be zero.
will be zero.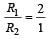 If same potential is applied on them, current in Ist will be half that in the later. If V potential is applied on them, current in them
If same potential is applied on them, current in Ist will be half that in the later. If V potential is applied on them, current in them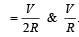
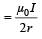
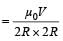
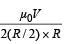
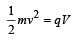 ..........(i)
..........(i)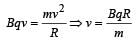 .......... (ii)
.......... (ii)