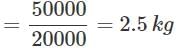Olympiad Test: Combustion & Flame - Class 8 MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test Science Class 8 - Olympiad Test: Combustion & Flame
What are the two main hydrocarbons present in L.P.G.?
What is the heat produced by burning 1 kg of fuel completely known as?
Which of the following has the highest calorific value?
Which of the following has the characteristics of a good fuel?
What is burning of a substance in the presence of air with the evolution of heat called?
When methane burns in air, what are the products formed?
Which of the following is a non- combustible substance?
What is the lowest temperature at which a substance starts burning called?
If the temperature falls below its ignition temperature, then what happens to the burning substance?
Which of the following is an example of rapid combustion?
In which of the following types of combustion are heat, light and sound produced?
What does the blue zone in an L.P.G. flame indicate?
Arrange the following fuels in the increasing order of their calorific value.
1. Hydrogen gas
2. Kerosine oil
3. Charcoal
4. Wood.
What does the incomplete combustion of a fuel give?
The total amount of heat produced by a fuel having a calorific value of 20 kJ/kg was found to be 50,000 joules. How much fuel was burnt?
When sufficient oxygen is not available, combustion of methane produces ____ gas and water.
|
90 videos|415 docs|44 tests
|