Important Questions (1 mark): Forces & Laws of Motion - UPSC MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test General Science(Prelims) by IRS Divey Sethi - Important Questions (1 mark): Forces & Laws of Motion
Identify the incorrect statement
Some of the leaves may get detached from a tree if we vigorously shake its branch because of
Essential characteristic of equilibrium is
“Inflated balloon lying on the surface of a floor moves forward when pierced with a pin. The above mentioned phenomenon is due to
Inertia is the property of a body by virtue of which the body is
To every action there is an,
The change in the momentum of a body in 0.01 second is 10 kg ms-1. The force acting on this body is
“Forces always occur in pairs”. From which law can we conclude the above statement?
Statement A: Rocket can propel its self in vacuum.
Statement B: Newton’s laws are universal.
Which of the two statements is true?
A high jumper runs for a while before taking high jump so that the inertia of __________ help him in taking a long jump.
A ball is dropped from a height of 10m. Ball is embedded in sand of 1m and stops.
Statement A: Gravitational force is the weakest force in nature
Statement B: Electrostatic force is the example of non – contact force
Which of the above two statement is true?
If P and Q are two bodies with masses 10 kg and 5kg respectively, then which body has more inertia?
‘Any two forces which are equal and opposite form an action and reaction pair’ The above statement is
Two bodies of masses 1kg and 5kg are dropped gently from the top of a tower. At a point 50cm from the ground both the bodies will have the same
Ayush hits a cricket ball which than rolls of a level ground after covering a short distance, the ball comes to rest. The ball slows to a stop because
In a football and stone of same size, the inertia of
A. Football is greater
B. Football is lesser
C. Stone is greater
D. Stone is lesser
“Action and reaction are equal and opposite but even then they do not cancel each other” the above statement is
Statement A: Calculus, a new branch of mathematics was stated by Newton.
Statement B: If mass remains same, doubling the force will reduce the acceleration to half.
Which of the above two statements is true
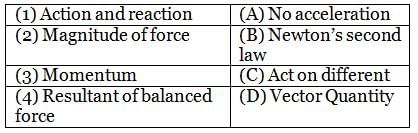
Match the following with correct response.
|
39 videos|110 docs|262 tests
|
|
39 videos|110 docs|262 tests
|


















