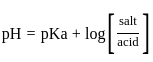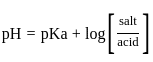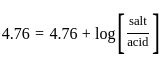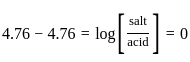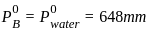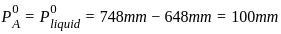MPTET Varg 1 Chemistry Mock Test - 2 - MPTET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - MPTET Varg 1 Chemistry Mock Test - 2
निर्देश: इन प्रश्नों में दिए गए वाक्यांशों के सही अर्थ को व्यक्त करने वाला शब्द (अनेक शब्दों के लिए एक शब्द) दिए गए विकल्पों में से चुनिए।
जो ममत्व से रहित हो
जो ममत्व से रहित हो
Choose the most appropriate antonym of the underlined word given in the sentence below:
There was jubilation in the crowd as the winning goal was scored.
Recently, in the BCCI Under-19 women's cricket tournament, Madhya Pradesh's girls' cricket team won the championship by defeating whom?
Which of the following statements describe Piaget and Vygotsky's views on language and thoughts correctly?
Match List-I with List-Il :
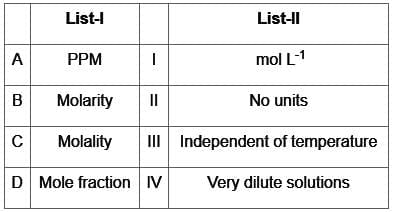
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
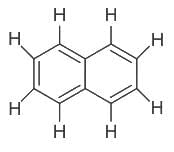
Number of π bonds and σ bonds in the following structure is–
Which of the following arrangements represent increasing oxidation number of the central atom?
For a given reaction, ∆H = 35.5 kJ mol–1 and ∆S = 83.6 JK–1 mol–1. The reaction is spontaneous at : (Assume that ∆H and ∆S do not vary with temperature)
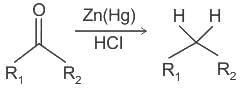
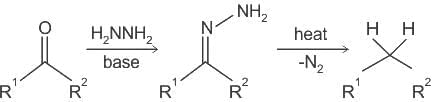
Reagents used in Clemmensen reduction and Wolff - Kishner reduction are respectively
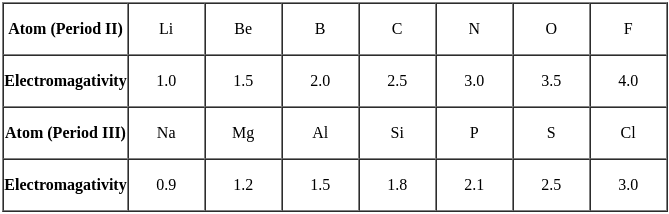
The electronegativity of N, O, P and S increases in the order
Which of the following Vitamins contains Cobalt?
Increasing order of the boiling points of CH3COOH (I), CH3CH2CH2OH (II) and CH3CHO (III) is in the order of
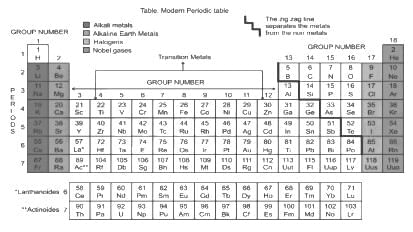
Which among the following elements has the largest atomic radii?
The pH of a 0.02 MNH4Cl solution will be
[Given Kb(NH4 OH) = 10-5 and log 2 = 0.301]The standard Gibbs energy for the given cell reaction in kJ mol-1 at 298 K is:
Zn(s) + Cu 2+ (aq) →Zn2+ (aq) + Cu(s)
E° = 2V at 298 K
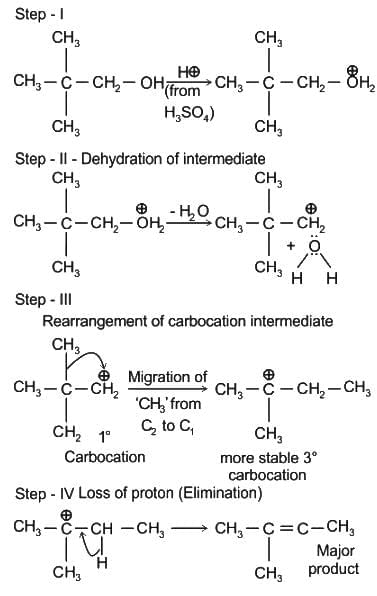
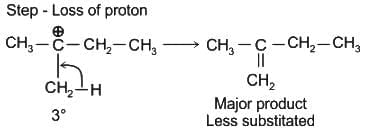
(Faraday’s constant, F = 96000 C mol-1)The major product on dehydration of (CH3)3C–CH2OH is:



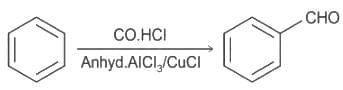
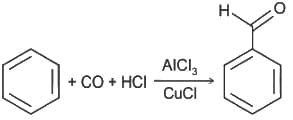
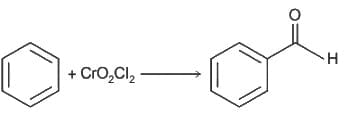
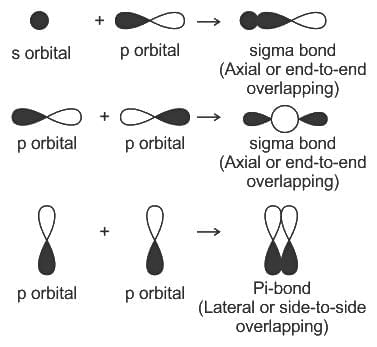
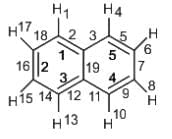
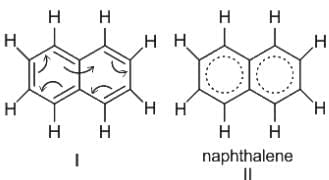
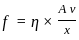
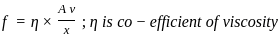
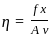
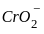
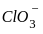
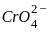
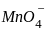
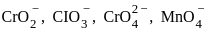
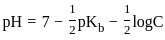
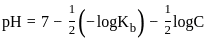 ----(1)
----(1) 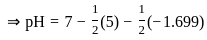
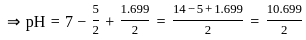
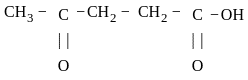
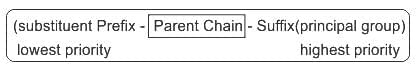
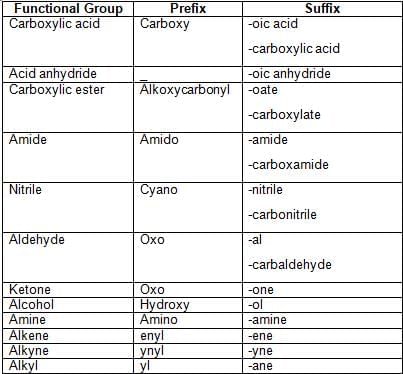
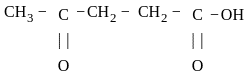
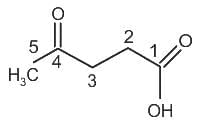
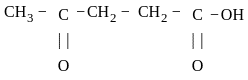 is 4-Oxopentanoic acid.
is 4-Oxopentanoic acid.