MPTET Varg 1 Chemistry Mock Test - 4 - MPTET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - MPTET Varg 1 Chemistry Mock Test - 4
"लक्ष्मी + छाया" का संधि-पद निम्नलिखित में से किस संधि का सही उदाहरण होगा?
निम्नलिखित में से 'ओस का मोती होना' मुहावरे का उचित अर्थ क्या है?
In which of the following types of communication the sender and receiver very rarely share the same time and space continuum and interact in a considerable way ?
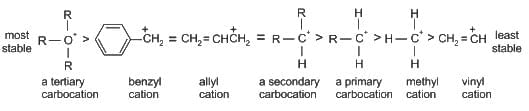
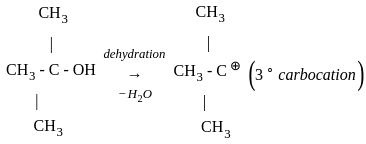
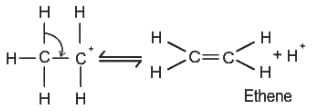
Which of the following compound gives the most stable carbonium ion during a dehydration reaction?
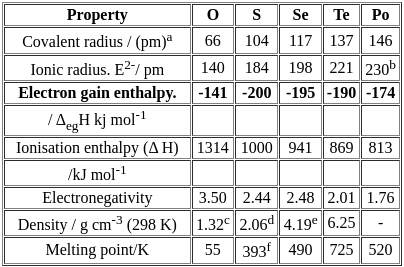
The correct order of negative electron gain enthalpy of group 16 elements is
The mixture of chloroxylenol and terpineol is used as-
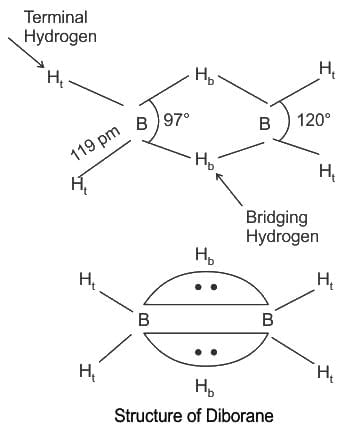
Which of the following statement is not correct about diborane?
KH value for Ar(g), CO2 (g), HCHO (g) and CH4 (g) are 40.39, 1.67, 1.83 × 10–5 and 0.413 respectively.
Arrange these gases in the order of their increasing solubility.
The correct order of solubility in water for He, Ne, Ar, Kr, Xe, is
What are the two impurities formed during the laboratory preparation of dinitrogen gas?
Which of the following is a true statement regarding calcination ________.
When a substance is dissolved in a solvent the vapour pressure of the solvent is decreased. This results in
Which of the following alkane cannot be made in good yield by Wurtz reaction?
Which amongst the following is incorrect statement?
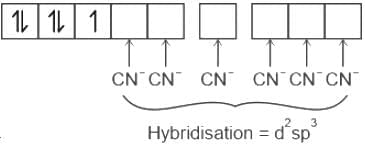
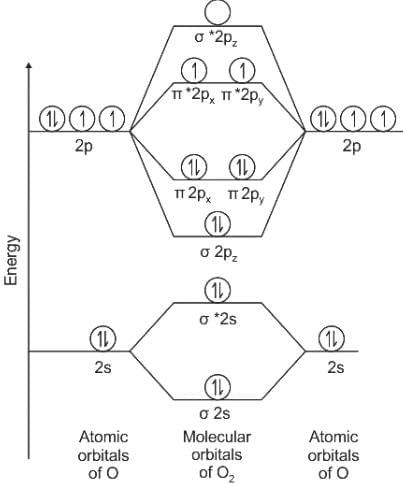
Which one of the following transition metal complex ions is expected to be coloured?




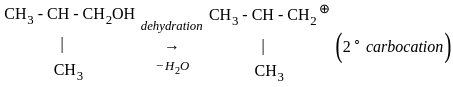
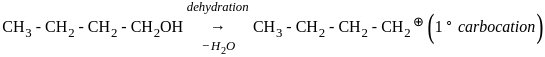
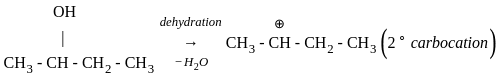
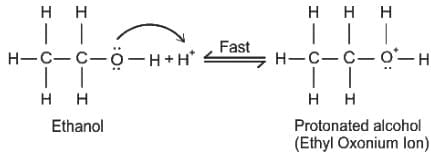
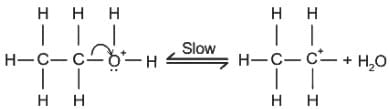
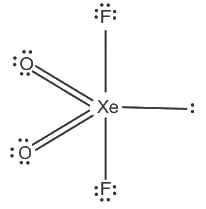
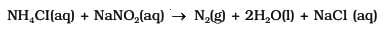
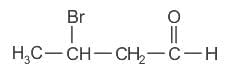
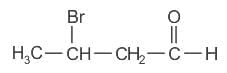
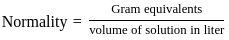



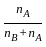
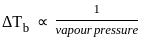
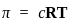
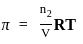
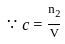 )
)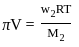
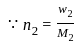 )
)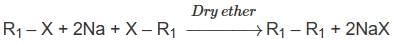
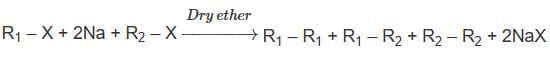
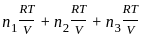
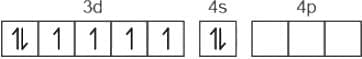
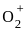 the total no. of electrons is 15 and configuration is
the total no. of electrons is 15 and configuration is 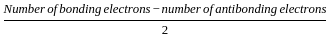
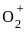 = 2.5
= 2.5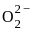 = 1
= 1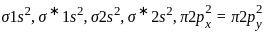
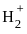 has only 1 electron.
has only 1 electron.