RSMSSB JE Civil Mock Test - 9 - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - RSMSSB JE Civil Mock Test - 9
Which Lok Devta of Rajasthan fought with Mahmud Ghaznavi?
Who among the following is called the first citizen of a State in India?
In which year was the RUDA (Rural Non Farm Development Agency-RUDA) established?
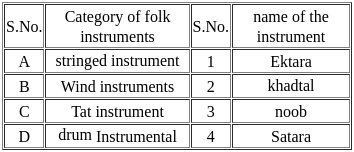
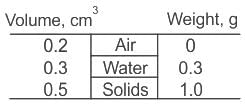
Match the following folk instruments of Rajasthan with their category -
Consider the following statements related to principles of design of connections:
- The centre of gravity of bolts should coincide with the centre of gravity of the connected members.
- The length of connection should be kept as small as possible.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
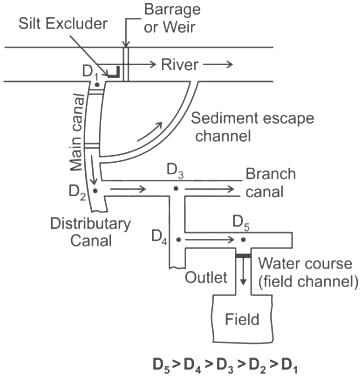
The outlet discharge factor is the duty at the head of :
Consider the following statements:
- Flexibility is the ratio of change of discharge in the distributing channel to the rate of change of the discharge in the outlet.
- A hyper-proportional outlet is the one in which the flexibility is greater than one.
- A sub-proportional outlet is the one in which the flexibility is less than one.
Which of the above statements are correct?
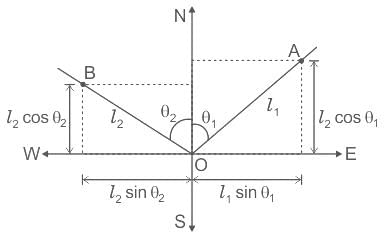
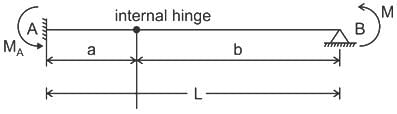
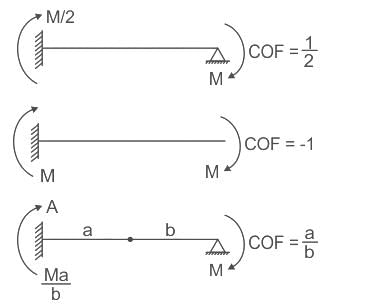
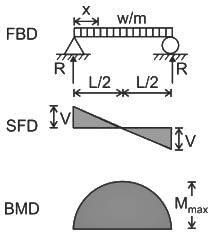
Carry-over factor CBA for the beam shown in the figure below is
Consider the following statements in relation to given sketch :
1. Soil is partially saturated at degree of saturation = 60%
2. Void ratio = 40%
3. Water content = 30%
4. Saturated unit weight = 1.5 g/cc.
Of these statements
The purpose of _______ test is to detect the presence of uncombined lime in cement.
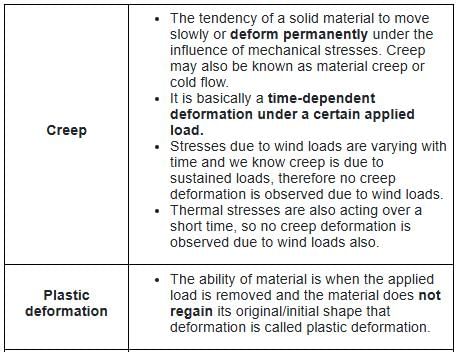
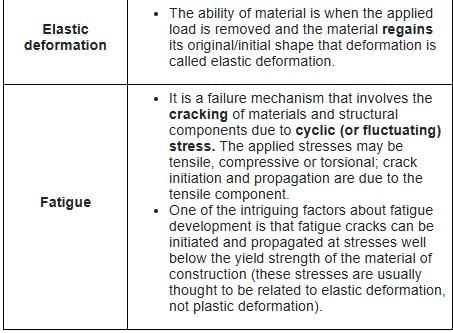
The failure of a material under varying load after a number of cycles of such load is known as
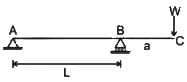
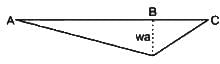
In a overhanging beam ABC, AB = L and BC = a, C being the free end. If it is subjected to a vertical load W at free end, maximum moment occurs at
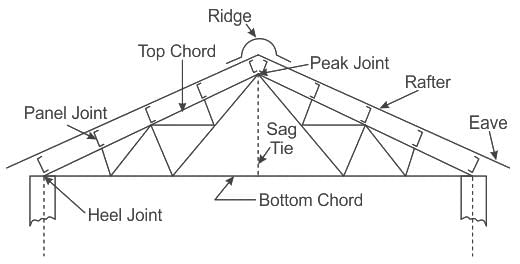
In which of the following truss members the stress depends upon whether the load is moving on top chord or bottom chord?
Improper curing leads to
I. Lower compressive and flexural strengths
II. Reduced durability
III. Ingress of chlorides and atmospheric chemicals
IV. Decrease in the rate of carbonation
Which of the following option is correct?
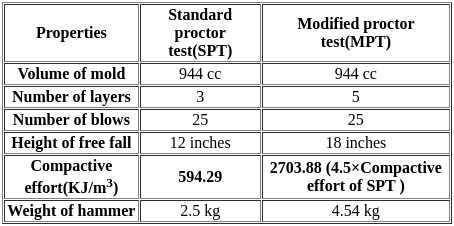
Let E2 and E1 represent compaction energy deployed for compacting the soil as per modified compaction test and standard test, as per IS.
Choose from the following correct ratio E2/E1:
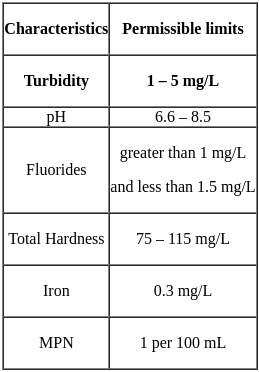
Consider the following statements:
1. Permissible limit for turbidity is between 1 - 5 ppm
2. Tintometer is used to measurement of taste and odour.
3. Total kjeldahl nitrogen is a measure of both organic and ammonia nitrogen.
Which of the above statement are correct related to water quality parameter?
Which of the following represents a correct match?
i) moveable hair method - The intercept on levelling staff is kept constant and stadia hair interval is variable.
ii) fixed hair method - The intercept on levelling staff is variable and stadia hair interval is fixed.
iii) tangential hair method - The stadia hairs are not used.
Fill in the blank with the CORRECT option:
_______ and _______ are the two major natural forces responsible for causing defects in timber.
Consider the following statement regarding reinforcement provision as per IS 456,
1. Minimum reinforcement for short column is 0.08% of gross area.
2. Minimum reinforcement for pedestal is 0.15 % of gross area.
3. The ratio of minimum reinforcement in vertical and horizontal directions of an RC wall is 3:5
4. Maximum reinforcement in the column is 4% of the gross area when splicing is not done.



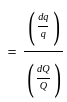
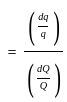 =
= 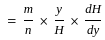
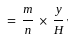 for semi-modular channel, dy = dH
for semi-modular channel, dy = dH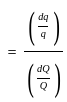 = 1
= 1 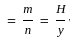 =
= 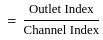
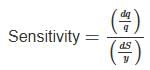
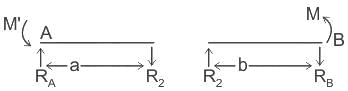
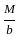 --------- (1)
--------- (1)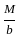 ------- (2)
------- (2)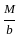 ×a - M' = 0
×a - M' = 0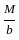 ×a--------(3)
×a--------(3)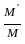 =
= 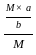 =
= 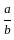
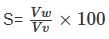
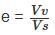
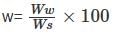
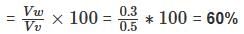
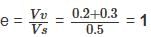
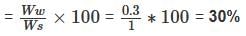
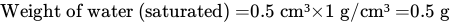
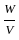 =
= 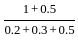 = 1.5 g/cc
= 1.5 g/cc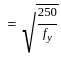 , f
, f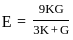
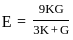
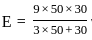
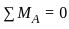
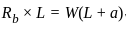
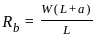
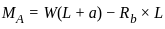
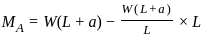
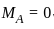
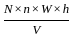
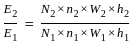 =
= 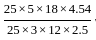 = 4.54
= 4.54