Test: Diabetes Mellitus & Insulinoma- 3 - NEET PG MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Diabetes Mellitus & Insulinoma- 3
Zinc transporter 8 antibody is seen in? (Recent Pattern Questions)
HNF-1β gene defect is seen in? (Recent Pattern Questions)
Which type of diabetes has impaired glucose induced secretion of insulin with preserved β cell mass? (Recent Pattern Questions)
Hyperglycemia is seen in all except? (Recall Pattern Questions)
Once a week preparation used in diabetes management is? (Recent Pattern Questions)
Which long acting insulin can be mixed with rapid acting insulin? (Recent Pattern Questions)
Which is the most common cause of death in type 2 diabetes mellitus? (Recent Pattern Questions)
The medical device shown below is used to deliver? (Recent Pattern Questions)

Which is the most common cause of death in type 1 diabetes mellitus? (Recent Pattern Questions)
A type 1 DM patient on insulin is having consistent values of Pre-breakfast hyperglycemia. Hence the physician ordered self- monitoring of blood glucose including at night. The following record of blood sugar of patient is given below. Which is the correct description for the recording shown below? (Recent Pattern Questions)

A diabetic normotensive patient of Enterococcus faecalis sepsis, on i.v. Linezolid developed high anion gap metabolic acidosis with increased serum lactate and negative ketone.
The acid base abnormality is most probably? (APPG 2016)
A middle aged man comes with RTA and bleeding from the scalp. He is unconscious. A card in his pocket reveals that he is a known diabetic on Glimipiride + Metformin 2 tablets twice daily. What should be the next step? (AIIMS May 2015)
A patient of hypoglycemia fails to regain consciousness after blood glucose is restored to normal. The complication to be suspected is? (UPSC 2015)
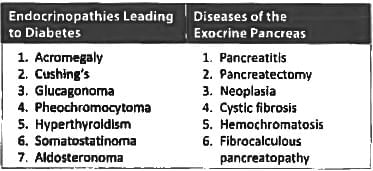
Consider the following conditions: (UPSC 2015)
a. Thyrotoxicosis, pheochromocytoma and acromegaly
b. Haemochromatosis
c. Conn’s syndrome (primary hyperaldosleronism)
d. Pancreatic carcinoma
Which of the above may result in secondary diabetes mellitus?
Common site of injection of islet cells in islet cell transplant for diabetes mellitus: (APPG 2015 Medicine)
Whipple’s triad is diagnostic of? (APPG 2015 Medicine)
A 50 year old patient with signs of peripheral neuropathy is found to have diabetes mellitus. He has no ocular symptoms. When would you refer this patient for retina evaluation? (UPSC 2015)
Which of the following is true about glycosylated haemoglobin? (JIPMER May 2015)
Which is related to MODY2? (JIPMER Nov 2015)
Initial imaging modality of choice for insulinoma? (JIPMER May 2015)
An obese lady aged 45 years was brought to emergency in a semi-comatose condition. The laboratory investigation showed K⁺ (5.8 m mol/L)i; Na⁺ (136 m mol/L); blood pH (7.1), HCO₃ (12 m mol/L) Ketone bodies (350 mg/dl). Probable blood glucose is? (AIPG 2011)
Oral anti-diabetic drug of choice in renal failure is: (Recent Pattern 2014-15)
A patient with DM of 4 years duration presents with dizziness and HR 52/min, Probable cause is: (Recent Pattern 2014-15)
Dose of insulin in diabetic nephropathy: (Recent Pattern 2014-15)
The most effective correction of acidosis in diabetic ketoacidosis is by: (Recent Pattern 2014-15)
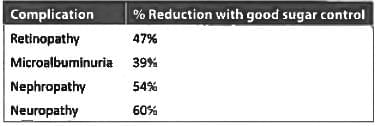
The complication of diabetes which cannot be prevented by strict control of blood sugar is: (Recent Pattern 2014-15)
Incorrect about gestational diabetes mellitus? (Recent Pattern 2014-15)
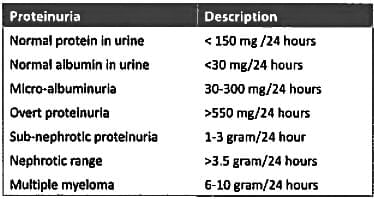
Microalbuminuria refers to urinary albumin excretion rate of: (Recent Pattern 2014-15)
Diabetes mellitus patient presents with HbA1C of 9.6%. All improve with tight glycemic control except: (Recent Pattern 2014-15)
Necrobiosis lipoidica is seen in: (Recent Pattern 2014-15)