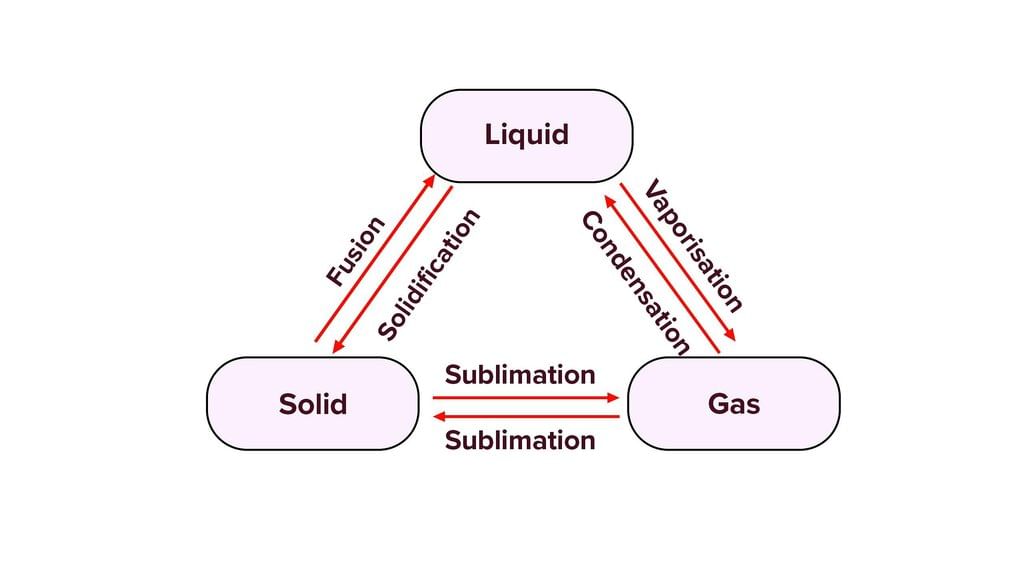
Grade 9 Exam > Grade 9 Tests > Test: Matter In Our Surroundings - 2 - Grade 9 MCQ
Test: Matter In Our Surroundings - 2 - Grade 9 MCQ
Test Description
15 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Matter In Our Surroundings - 2
Test: Matter In Our Surroundings - 2 for Grade 9 2025 is part of Grade 9 preparation. The Test: Matter In Our Surroundings - 2 questions and answers have been prepared
according to the Grade 9 exam syllabus.The Test: Matter In Our Surroundings - 2 MCQs are made for Grade 9 2025 Exam.
Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests for Test: Matter In Our Surroundings - 2 below.
Solutions of Test: Matter In Our Surroundings - 2 questions in English are available as part of our course for Grade 9 & Test: Matter In Our Surroundings - 2 solutions in
Hindi for Grade 9 course.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Grade 9 Exam by signing up for free. Attempt Test: Matter In Our Surroundings - 2 | 15 questions in 20 minutes | Mock test for Grade 9 preparation | Free important questions MCQ to study for Grade 9 Exam | Download free PDF with solutions
Test: Matter In Our Surroundings - 2 - Question 1
Which of the following statements is incorrect?
Detailed Solution for Test: Matter In Our Surroundings - 2 - Question 1
Test: Matter In Our Surroundings - 2 - Question 2
On converting 25°C, 38°C and 66°C to Kelvin scale, the correct sequence of temperature will be
Detailed Solution for Test: Matter In Our Surroundings - 2 - Question 2
Test: Matter In Our Surroundings - 2 - Question 3
Shivam visited an LPG unit and found that the gas can be liquified at specific conditions of temperature and pressure. Help him to identify the correct set of conditions.
Detailed Solution for Test: Matter In Our Surroundings - 2 - Question 3
Test: Matter In Our Surroundings - 2 - Question 4
The property to flow is unique to fluids. Which one of the following statements is correct?
Detailed Solution for Test: Matter In Our Surroundings - 2 - Question 4
Test: Matter In Our Surroundings - 2 - Question 5
Which of the following is correct order of forces of attraction?
Detailed Solution for Test: Matter In Our Surroundings - 2 - Question 5
Test: Matter In Our Surroundings - 2 - Question 6
Which condition out of the following will increase the evaporation of water?
Detailed Solution for Test: Matter In Our Surroundings - 2 - Question 6
Test: Matter In Our Surroundings - 2 - Question 7
Choose the correct statement out of the following.
Detailed Solution for Test: Matter In Our Surroundings - 2 - Question 7
Test: Matter In Our Surroundings - 2 - Question 8
Which one of the following sets of phenomenon would increase on raising the temperature?
Detailed Solution for Test: Matter In Our Surroundings - 2 - Question 8
Detailed Solution for Test: Matter In Our Surroundings - 2 - Question 9
Detailed Solution for Test: Matter In Our Surroundings - 2 - Question 10
Test: Matter In Our Surroundings - 2 - Question 11
Which of the following does not undergo sublimation?
Detailed Solution for Test: Matter In Our Surroundings - 2 - Question 11
Detailed Solution for Test: Matter In Our Surroundings - 2 - Question 12
Detailed Solution for Test: Matter In Our Surroundings - 2 - Question 13
Test: Matter In Our Surroundings - 2 - Question 14
Which process involves the transformation of gas directly into a solid?
Detailed Solution for Test: Matter In Our Surroundings - 2 - Question 14
Test: Matter In Our Surroundings - 2 - Question 15
What effect does increasing temperature have on the kinetic energy of particles?
Detailed Solution for Test: Matter In Our Surroundings - 2 - Question 15
Information about Test: Matter In Our Surroundings - 2 Page
In this test you can find the Exam questions for Test: Matter In Our Surroundings - 2 solved & explained in the simplest way possible.
Besides giving Questions and answers for Test: Matter In Our Surroundings - 2, EduRev gives you an ample number of Online tests for practice
Download as PDF