Test: Transpiration - Class 10 MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Transpiration
What is the primary function of guard cells in relation to stomata?
What is the relationship between transpiration and temperature?
Which type of transpiration involves water vapor escaping directly from the leaf surface?
Which part of the plant is primarily responsible for stomatal transpiration?
Which of the following adaptations would help a plant reduce water loss?
Which type of transpiration occurs through small openings on old stems?
What defines the difference between transpiration and bleeding?
What is the difference between transpiration and evaporation?
Which environmental condition would likely decrease the rate of transpiration?
What adaptation do many plants in dry climates have to minimize transpiration?
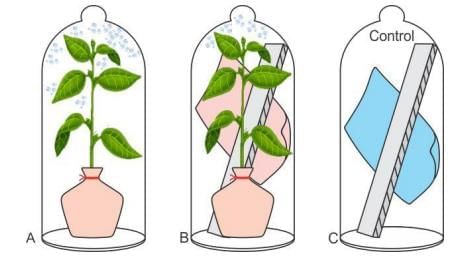
In which experiment did condensation appear on the inner wall of the bell jar, indicating transpiration?


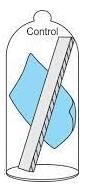
What happens to the cobalt chloride paper in Setup B of the transpiration experiment?