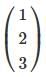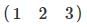CUET PG Commerce Mock Test - 2 - CUET PG MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test Commerce CUET PG Mock Test Series 2026 - CUET PG Commerce Mock Test - 2
From the following statements of Assertion (A) and Reason (R), indicate the correct codes.
Assertion (A) : A reasonable sized sample drawn randomly from large sized population contains almost all the characteristics which exist in the population.
Reason (R) : The theory of sampling based on the two important laws of statistics, viz, law of statistical regularity and law of inertia of large numbers.
Bank overdraft payable on demand should be treated as cash and cash equivalent according to which one of the following Accounting Standard?
Match List I with List II
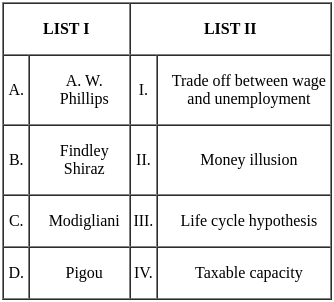
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
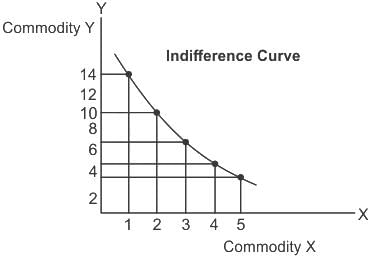
In case of indifference curve of two goods X and Y, as consumption of X increases:
Arrange the following steps involved in the process of IPO issue in correct order.
(A) Verification by SEBI
(B) Hiring an under writer
(C) Registration for IPO
(D) Pricing of IPO
(E) Allotment of shares
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Which of the following are primary functions of Commercial Banks?
(A) Accepting Deposits
(B) Agency Service
(C) Discounting Trade Bills
(D) Financing Foreign Trade
(E) General Utility Service
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Arrange the following Financial Institution in the increasing order of their date of establishment-
(A) NABARD
(B) EXIM Bank
(C) UTI
(D) SIDBI
(E) ECGC
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Which of the following are integral dimensions of a firm's credit policy?
(A) Credit Standards.
(B) Credit appraisal
(C) Credit period.
(D) Cash discount
(E) Collection policy
Choose the most appropriate from the options given below:
Consider the following statements:
- Prior to liberalization, India had a floating exchange rate system.
- Government companies can be converted into private companies by outright sale only.
- Removal of mandatory convertibility clause and abolition of phased manufacturing programmes for new projects are important features of the LPG Policy 1991
- Post liberalization, Monopolies and Restrictive Trade Practices (MRTP) Act was replaced by the Competition Act
Which of the above statements is/ are correct?
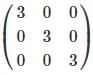
A matrix having only m rows and one column is called:
Arrange the following in order of its sequence in decision making process
(A) Analyze the alternatives
(B) Generate multiple alternatives
(C) Recognize that a decision needs to be made
(D) Implement the selected alternative
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Four Ps concept takes the seller's view of the market, not the buyer's view. From the buyer's viewpoint, four Ps are described as four As.
Match List-I (Four Ps) with List-II (Four As)
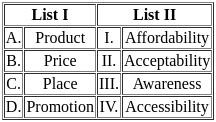
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Match List-I (Retailer Type) with List-II (Description)
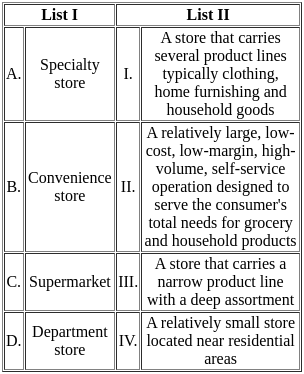
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Arrange the alternative concepts under which organizations design their marketing strategies in order of the evolution
(A) Product Concept
(B) Production Concept
(C) Selling Concept
(D) Marketing Concept
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Arrange the following steps of selling process in correct order.
(A) Prospecting and qualifying
(B) Preapproach then approach.
(C) Presentation and demonstration
(D) Handling objections, closing, and follow-up
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Which of the following are the possible objectives of Informative Advertising?
(A) Communicating customer value
(B) Telling the market about a new product
(C) Maintaining customer relationships
(D) Explaining how a product works
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Advertising appeals should have which of the following characteristics?
(A) Entertaining
(B) Meaningful
(C) Distinctive
(D) Believable
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Accounting standards deal with various aspects of accounting events..Arrange it in proper sequence
(A) the disclosures relating to these transactions and events
(B) presentation of these transactions and events in the financial statements
(C) recognition of events and transactions in the financial statements
(D) measurement of these transactions and events
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
If goods are invoiced to the branch at cost, the trading results of branch can be ascertained by which of the following methods:
(A) Debtors Method
(B) Trading and Profit and Loss Account (Final Account) method
(C) Stock and Debtors method
(D) Whole sale branches method
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Match List-I (Term) with List-II (Explanation)
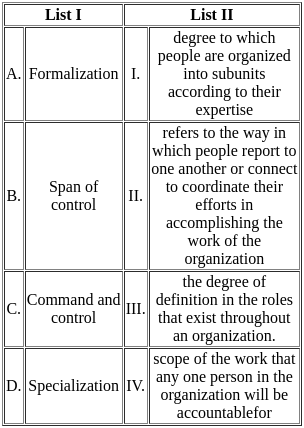
Choose the correct answer from the options given below: