CUET PG Psychology Mock Test - 1 - CUET PG MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - CUET PG Psychology Mock Test - 1
Arrange the correct sequence in Simple Random Sampling:
(A) Select 'n' cases randomly (with the help of fishbowl method or a random number table)
(B) Determine the Size of the Present Population
(C) Decide on the Sample size (n)
(D) Identify sampling units in the population.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(A) Select 'n' cases randomly (with the help of fishbowl method or a random number table)
(B) Determine the Size of the Present Population
(C) Decide on the Sample size (n)
(D) Identify sampling units in the population.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Highly cohesive groups often assume that they can do no wrong and that information contrary to the group’s view should be rejected. This tendency is known as-
Conditioned and unconditioned stimuli begin and end at the same time. This process is called _______.
______ memory includes what people can do or demonstrate, whereas _____ memory is about what people know and can report.
According to B. F. Skinner the basic mechanism for controlling human behavior is:
The Cognitive Behavior Therapy proposed by Beck, proposes the following trajectory of illness:
(A) Illogical ideas e.g. tendency to overgeneralise setbacks
(B) Depression
(C) Negative behavior in terms of ideas and thoughts
(D) Negative affect
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
The characteristics of a fully functioning person are:
(A) aware of all experiences
(B) able to face difficulties
(C) inhibited and not free to make choices
(D) adapt to the changing environmental conditions.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
As an object gets closer, its visual angle becomes ______ and its retinal image gets _______.
Unlike the Standford- Binet, the Weschler test provides:
Which of the following is not a depth cue that is potentially available for only one eye?
A type of experimental research in which neither the subjects nor the person who directly deals with the subjects for the experimenter knows the specifics of the experiment is
A child whose actions are motivated by an avoidance of punishment shows which level of moral development?
Raghu was walking along the river when he was bitten by a snake. Now he is afraid not only of snakes, but also of walking near the river. This is an example of:
The method of combination works on the basis of successive rather than simultaneous is called __________.
Match List I with List II
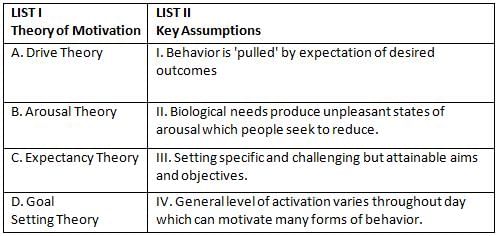
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Foundations of knowledge based on logic, processes of reason and a knowable singular reality, is characteristic of _____________ era
According to Path Goal Leadership theory, the leader who sets challenging goals for associates and shows confidence that they will attain these goals and perform well is called:
If you look up the address of a person you have never visited before and three minutes later can no longer remember the address, you should conclude that the information was probably held in:
A very brief memory created in a split-second sight is called _____
Match List I with List II
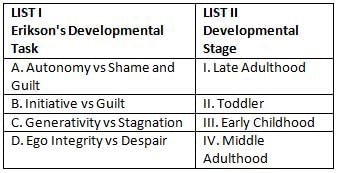
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
A parent who fails to set firm limits on age appropriate behavior required for a young child would be using which parenting style?
Which of the following is not a neurotransmitter ?
Parul remembers things from the past very well but cannot incorporate present events into her memory. She is suffering from:














