CUET PG Psychology Mock Test - 2 - CUET PG MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - CUET PG Psychology Mock Test - 2
According to Piaget’s theory of cognitive development, the earliest development stage from those listed below is :
The term ‘employee turnover’ is related to which of the following issues?
Fluency, flexibility and originality are characteristics of _______
Information organised in Long Term Memory (LTM) stores is aided by the reminders which direct memory search to appropriate parts of the LTM repository. These are called:
The tendency to go along with the group in order to fulfill the group’s expectation and gain acceptance is
Relatively rare disorder where accumulation of an abnormal amount of cerebrospinal fluid within the cranium causing damage to the brain tissue and enlargement of the skull.
Psychological research on everyday human concerns reveals that:
When Libido is attached to or invested in an object, it is known as:
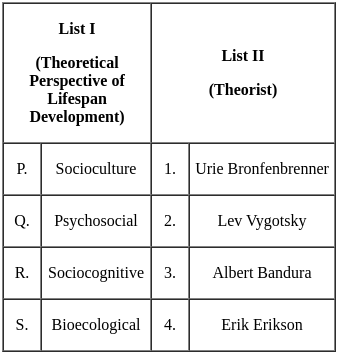
Match List I with List II and select the correct answer using the codes given below :
The behavior of avoiding a noxious stimulus by a responder is called:
Reliability of psychological test is ascertained by :
(I) Studying the association of the test with itself.
(II) Studying the association of the test with another test
T-Groups are known as an organizational intervention technique, known for :
Conscious forcing of desires or thoughts out of consciousness is called:
Which of the following are not true in the context of General and Fluid Intelligence?
A. Fluid intelligence is the basic capacity for learning and problem solving
B. Fluid Intelligence is the product of interaction of person with their environment.
C. It consists of learned skills.
D. Is investment theory of intelligence.














