CUET PG Psychology Mock Test - 3 - CUET PG MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - CUET PG Psychology Mock Test - 3
A neurological disorder characterized by sleep at inappropriate times is called-
Any environment agent that causes damage during prenatal period is:
Ravi believes that experiences throughout his life continually change his personality. Which theorist would probably not agree with it?
Which among the following is not a collectivistic view of the self ?
Which perspective maintains that most human perceptual capabilities are inborn and that result very little from learning?
Which school of Philosophy would favour the statement, ‘‘Since both pain and pleasure are the wealth of man, they are his good teachers’’ ?
Which of the following describes the path of a neural impulse from the sense organs to the brain?
(A) Optic Nerve
(B) Receptor Cells
(C) Ganglion Cells
(D) Bipolar Cells
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
A language structure located in the left temporal lobe of the cerebral cortex that plays a role in comprehending word meaning is
Psychology should emphasize each person's unique potential for psychological growth and self directedness is
The component of personality that is a vast reservoir of basic biological urges is the:
Which of the following are correct regarding the humanist psychology?
(A) Focuses on personology
(B) Regarded as the 3rd force
(C) Is not a school of thought
(D) Talks about deficiency needs
Match List I with List II
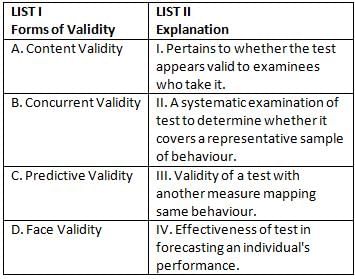
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
The field of Artificial Intelligence is most closely related to which psychological approach?
Abraham Maslow’s hierarchy of needs includes which of the following except
EEG recording of the REM sleep is characterized by



















