NEET PG Exam > NEET PG Tests > Test: Chemistry and Metabolism of Amino Acids- 4 - NEET PG MCQ
Test: Chemistry and Metabolism of Amino Acids- 4 - NEET PG MCQ
Test Description
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Chemistry and Metabolism of Amino Acids- 4
Test: Chemistry and Metabolism of Amino Acids- 4 for NEET PG 2025 is part of NEET PG preparation. The Test: Chemistry and Metabolism of Amino Acids- 4 questions and answers have been prepared
according to the NEET PG exam syllabus.The Test: Chemistry and Metabolism of Amino Acids- 4 MCQs are made for NEET PG 2025 Exam.
Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests for Test: Chemistry and Metabolism of Amino Acids- 4 below.
Solutions of Test: Chemistry and Metabolism of Amino Acids- 4 questions in English are available as part of our course for NEET PG & Test: Chemistry and Metabolism of Amino Acids- 4 solutions in
Hindi for NEET PG course.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET PG Exam by signing up for free. Attempt Test: Chemistry and Metabolism of Amino Acids- 4 | 20 questions in 20 minutes | Mock test for NEET PG preparation | Free important questions MCQ to study for NEET PG Exam | Download free PDF with solutions
Test: Chemistry and Metabolism of Amino Acids- 4 - Question 1
N-acetyl-cysteine replenishes: (JIPMER 2012)
Detailed Solution for Test: Chemistry and Metabolism of Amino Acids- 4 - Question 1
*Multiple options can be correct
Test: Chemistry and Metabolism of Amino Acids- 4 - Question 2
Which of the following is true about Glutathione?
Detailed Solution for Test: Chemistry and Metabolism of Amino Acids- 4 - Question 2
Test: Chemistry and Metabolism of Amino Acids- 4 - Question 3
In glutathione which amino acid is reducing agent? (AIIMS June 1997)
Detailed Solution for Test: Chemistry and Metabolism of Amino Acids- 4 - Question 3
Detailed Solution for Test: Chemistry and Metabolism of Amino Acids- 4 - Question 4
Detailed Solution for Test: Chemistry and Metabolism of Amino Acids- 4 - Question 5
Test: Chemistry and Metabolism of Amino Acids- 4 - Question 6
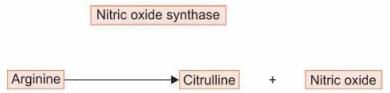
True about Nitric Oxide are all except:
Detailed Solution for Test: Chemistry and Metabolism of Amino Acids- 4 - Question 6
Test: Chemistry and Metabolism of Amino Acids- 4 - Question 7
Creatinine is formed from: (PGI June 06)
Detailed Solution for Test: Chemistry and Metabolism of Amino Acids- 4 - Question 7
Test: Chemistry and Metabolism of Amino Acids- 4 - Question 8
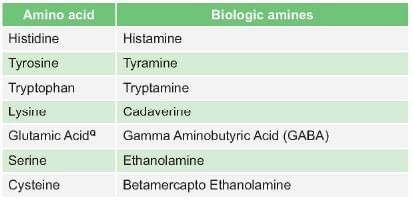
Histidine is converted to Histamine by which reaction:
Detailed Solution for Test: Chemistry and Metabolism of Amino Acids- 4 - Question 8
Test: Chemistry and Metabolism of Amino Acids- 4 - Question 9
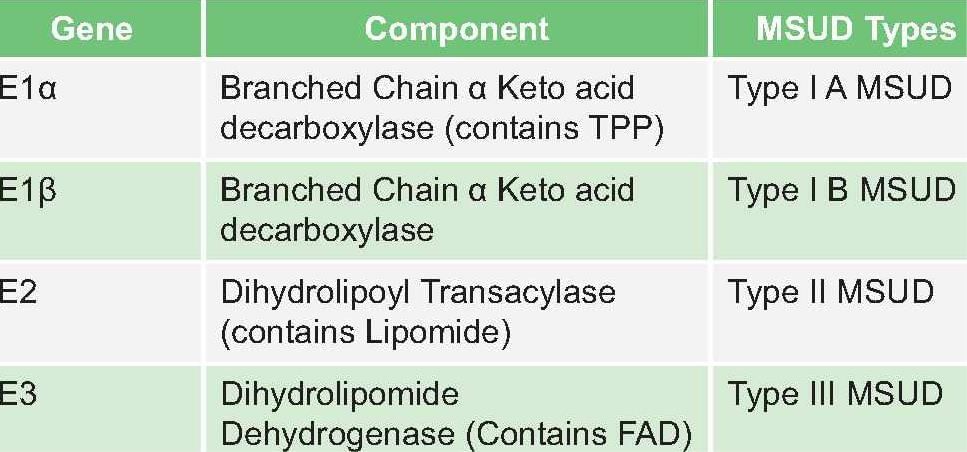
Branched chain ketoacid decarboxylation is defective in: (AI 2010)
Detailed Solution for Test: Chemistry and Metabolism of Amino Acids- 4 - Question 9
Test: Chemistry and Metabolism of Amino Acids- 4 - Question 10
MSUD type I A is due to mutation of:
Detailed Solution for Test: Chemistry and Metabolism of Amino Acids- 4 - Question 10
Test: Chemistry and Metabolism of Amino Acids- 4 - Question 11
Which is not formed from branched chain amino acid? (Latest Q)
Detailed Solution for Test: Chemistry and Metabolism of Amino Acids- 4 - Question 11
Test: Chemistry and Metabolism of Amino Acids- 4 - Question 12
Treatment used in Isovaleric Aciduria: (Latest Q)
Detailed Solution for Test: Chemistry and Metabolism of Amino Acids- 4 - Question 12
Test: Chemistry and Metabolism of Amino Acids- 4 - Question 13
Which of the following amino acid is excreted in urine in maple syrup urine disease: (AI 1999)
Detailed Solution for Test: Chemistry and Metabolism of Amino Acids- 4 - Question 13
*Multiple options can be correct
Test: Chemistry and Metabolism of Amino Acids- 4 - Question 14
Diseases of branched chain amino acid includes: (PGI Nov 2013)
Detailed Solution for Test: Chemistry and Metabolism of Amino Acids- 4 - Question 14
Test: Chemistry and Metabolism of Amino Acids- 4 - Question 15
The nitrogen atom of aspartate formed from asparagines using enzyme asparaginase is from:
Detailed Solution for Test: Chemistry and Metabolism of Amino Acids- 4 - Question 15
Detailed Solution for Test: Chemistry and Metabolism of Amino Acids- 4 - Question 16
Test: Chemistry and Metabolism of Amino Acids- 4 - Question 17
Amino acid responsible for Thioredoxin reductase activation:
Detailed Solution for Test: Chemistry and Metabolism of Amino Acids- 4 - Question 17
Test: Chemistry and Metabolism of Amino Acids- 4 - Question 18
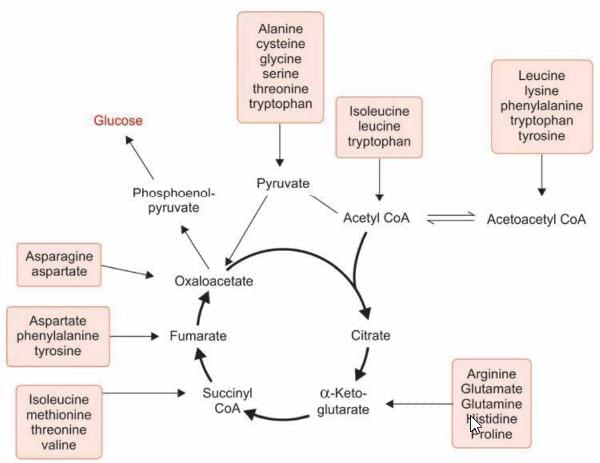
Oxaloacetate is derived from which amino acids:
Detailed Solution for Test: Chemistry and Metabolism of Amino Acids- 4 - Question 18
Test: Chemistry and Metabolism of Amino Acids- 4 - Question 19
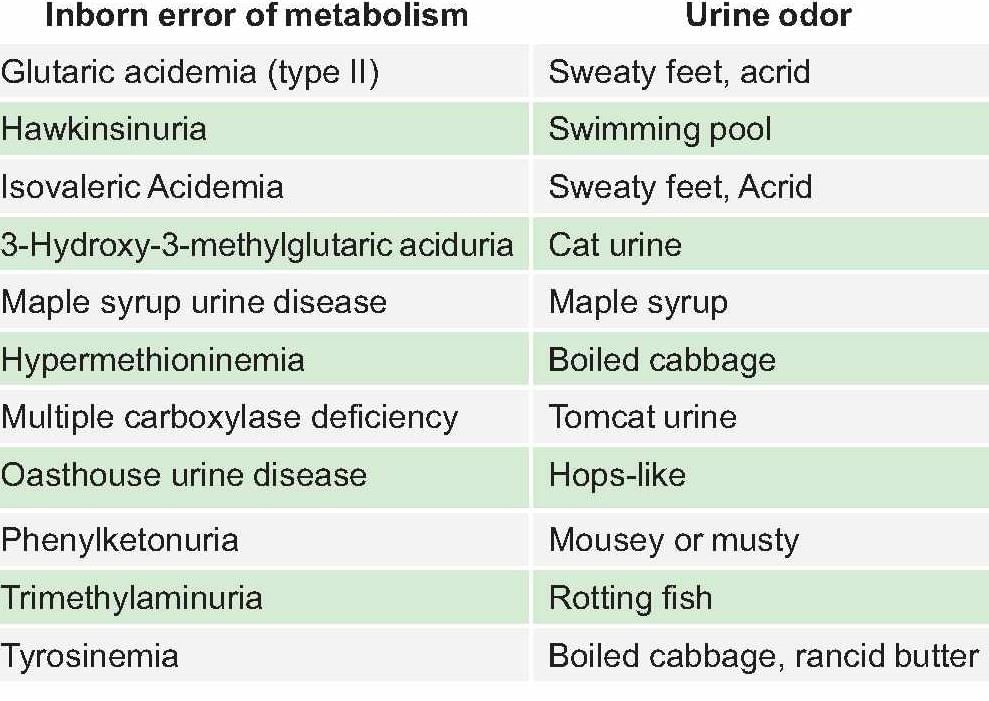
Smell of sweaty feet is seen in:
Detailed Solution for Test: Chemistry and Metabolism of Amino Acids- 4 - Question 19
Test: Chemistry and Metabolism of Amino Acids- 4 - Question 20
During the formation of hydroxyl proline and hydroxyl lysine, the essential factors required is/ are: (PGI Dec 2003)
Detailed Solution for Test: Chemistry and Metabolism of Amino Acids- 4 - Question 20
Information about Test: Chemistry and Metabolism of Amino Acids- 4 Page
In this test you can find the Exam questions for Test: Chemistry and Metabolism of Amino Acids- 4 solved & explained in the simplest way possible.
Besides giving Questions and answers for Test: Chemistry and Metabolism of Amino Acids- 4, EduRev gives you an ample number of Online tests for practice
Download as PDF