Previous Year Questions: Economics- 1 - UPSC MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Previous Year Questions: Economics- 1
The Phillip’s curve is the schedule showing the relationship between
A firm practising price discrimination will be
Minimum payment of factor of production is called
In a capitalistic economy the prices are determined by
A 'want' becomes a 'demand' only when it is backed by the
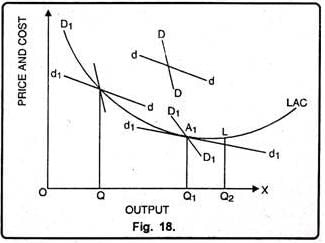
Under which market condition do firms have excess capacity?
“Economics is what it ought to be”. This statement refers to
Which one of the following is NOT a method of measurement of National Income?
Labour intensive technique would get choosen in a
Surplus earned by a factor other than land in the short period is referred to as
If two commodities are complements, then their cross-price elasticity is
Opportunity cost of production of a commodity is
Which one of the following is a developmental expenditure?
The national income consists of a collection of goods and services reduced to common basis by being measured in terms of money. Who says this?
All of the goods which are scarce and limited in supply are called
Engel’s Law states the relationship between
An expenditure that has been made and cannot be recovered is called
Seawater, fresh air etc are regarded in economics as
Excise duty on a commodity is payable with reference to its