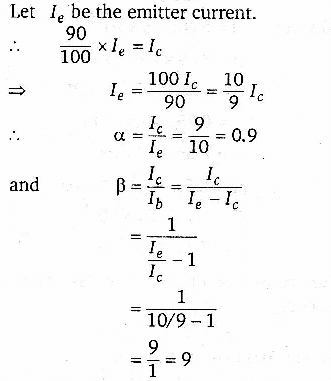BITSAT Practice Test - 12 - JEE MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test BITSAT Mock Tests Series & Past Year Papers 2025 - BITSAT Practice Test - 12
Which of the following is used as a coolant in automobile radiator as well as a heater in hot water bags?
If force(F), time(T) and velocity(V) are treated as fundamental quantities then dimensional formula of energy will be
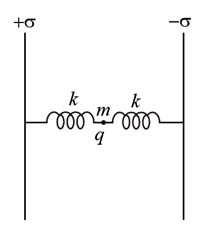
Two large conducting plates having surface charge densities + σ & –σ are fixed d distance apart. A small test charge q of mass m is attached to two identical springs as shown in the adjacent figure. The charge q is now released from rest with springs in natural length. Then q will [neglect gravity]:

In a radioactive decay process, the negatively charged emitted β- particles are
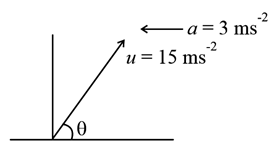
A boy throws a ball upwards with velocity u = 15 m s−1. The wind imparts a horizontal acceleration of 3 m s−2 to the left. The angle θ¸ at which the ball must be thrown so that the ball returns to the boy's hand is (use g = 10 m s−2)
An electromagnetic wave is propagating along Y-axis. Then
A long straight wire is placed along the axis of a circular ring of radius R. The mutual inductance of this system is
The effect of rotation of the earth on the value of acceleration due to gravity is
A variable force, given by the 2-dimensional vector 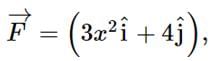 acts on a particle. The force is in newton and x is in metre. What is the change in the kinetic energy of the particle as it moves from the point with coordinates (2, 3) to (3, 0)? (The coordinates are in metres)
acts on a particle. The force is in newton and x is in metre. What is the change in the kinetic energy of the particle as it moves from the point with coordinates (2, 3) to (3, 0)? (The coordinates are in metres)
The surface that is chosen for the application of Gauss's law is called
The inductance of a closed-packed coil of 400 turns is 8 mH. A current of 5 mA is passed through it. The magnetic flux through each turn of the coil is
Assertion: A body whatever its motion is always at rest in reference frame which is fixed to the body itself.
Reason: The relative velocity of a body with respect to itself is always zero.
A bus starts to move with an acceleration of 1 m/s2. A man, who is 48 m behind the bus, runs to catch it with a constant velocity of 10 m/s. In how much time will he catch the bus?
Blocks A and B of masses 2m and m are connected as shown in the figure. The spring has negligible mass. The string is suddenly cut. The respective magnitudes of acceleration of masses 2m and m at that instant are
A solid cylinder of mass M and radius R is mounted on a frictionless horizontal axle, so that it can freely rotate about this axis. A string of negligible mass is wrapped round the cylinder and a body of mass m is hung from the string as shown in the figure. The mass is released from rest.
The acceleration with which the mass will fall is
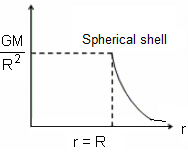
In case of a spherical shell having radius R and mass M, which of the following graphs between gravitational intensity and distance is true?
A wooden block, with a coin placed on its top, floats in water as shown in the figure. The distance h and l are shown there. After sometime, the coin falls into the water. Then,
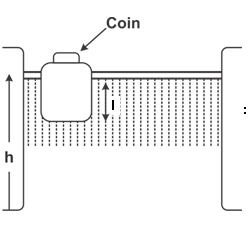 :
:
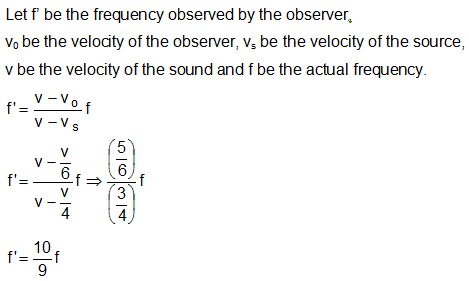
If a source emitting waves of frequency f moves towards an observer with a velocity v/4 and the observer moves away from the source with a velocity v/6. The apparent frequency as heard by the observer will be
(v = Velocity of sound)
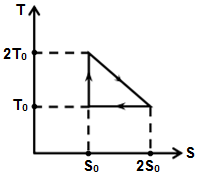
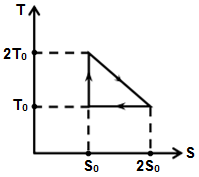
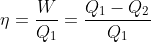
The temperature-entropy diagram of a reversible engine cycle is given in the figure. Its efficiency is
The point charges 3μC and 4μC are placed at a separation of 7 m. The medium between them is of two type as shown in figure. What is the electric force acting between them?
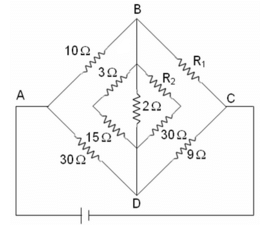
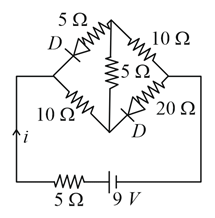
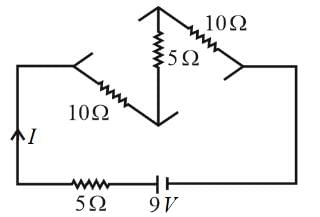
In the Wheatstone's bridge shown below, in order to balance the bridge, we must have
A thin wire loop carrying a current I is placed in a uniform magnetic field B pointing out of the plane of the coil as shown in the figure. The loop will tend to
A galvanometer of 50 Ω resistance has 25 divisions. A current of 4 x 10-4 A gives a deflection of one division. To convert this galvanometer into a voltmeter having a range of 25 V, it should be connected with a resistance of
The voltage 7.25 sin (300t) is applied to a series RLC circuit with R = 120 ohms, L = 0.140 H and C = 1.45 μF. What is the impedance Z and the phase angle θ?
A person can see clearly only up to a distance of 30 cm. He wants to read a book placed at a distance of 50 cm from his eyes. What is the power of the lens he requires for his spectacles?
When a certain metallic surface is illuminated with monochromatic light of wavelength λ, the stopping potential for photoelectric current is 3V0. When the same surface is illuminated with light of wavelength 2λ, the stopping potential is V0. The threshold wavelength for this surface for photoelectric effect is
In an n-p-n transistor amplifier, the collector current is 9 mA. If 90% of the electrons from the emitter reach the collector, then
|
2 videos|17 docs|85 tests
|
|
2 videos|17 docs|85 tests
|




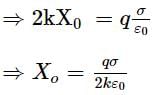
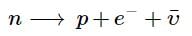
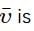 the antineutrino.
the antineutrino.
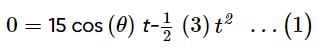
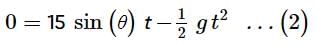
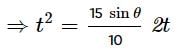
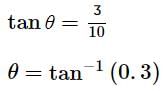
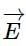 and as well as to the magnetic field
and as well as to the magnetic field 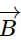 as shown below.
as shown below.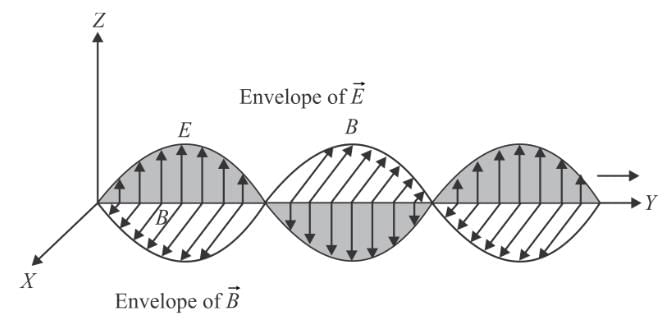
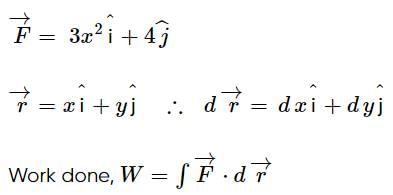

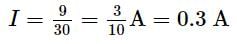
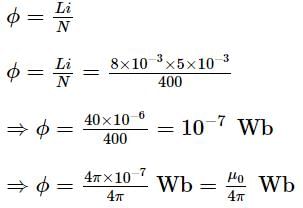


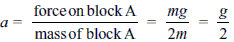
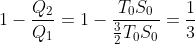
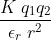
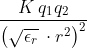
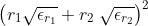
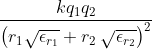
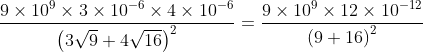

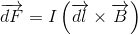
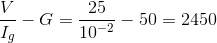 ohm in series
ohm in series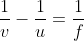 gives f = -75 cm.
gives f = -75 cm.