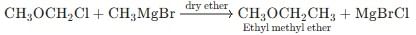VITEEE Chemistry Test - 3 - JEE MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - VITEEE Chemistry Test - 3
Primary and secondary alcohols on action of red hot copper give
In the reaction, CH₃CHO + HCN → X, a chiral centre is introduced. The product X is
The cyanohydrin of a compound X on hydrolysis gives lactic acid; The X is
Electrophile in the case of chlorination of benzene in presence of FeCl₃ is
How many molecules are present in one gram of hydrogen gas?
Which compound can exist in a dipolare (Zwitterion) structure?
In a reaction involving ring substitution of C6H5Y, the major product is meta isomer. The group Y can be
The reaction N₂ + O₂ → 2NO is endothermic . The forward reaction is
If a gas at constant temperature and pressure expands, then its
Drug which helps to reduce anxiety and brings about calmness is
The IUPAC name for the complex
[ Co(NO2)(NH3)5 ]Cl2 is :
Which of the following complexes will be formed in the brown ring test for nitrates
In the diazotisation of aniline with sodium nitrite and hydrochloric acid, the excess of hydrochloric acid is used primarily to
The quanitity of electricity required to librate 112 cm3 of hydrogen at STP from acidified water is
An electrolytic cell contains a solution of Ag₂SO₄ and has Pt electrodes.A current is passed till 1.6 g of O₂ has been liberated at anode. The amount of silver deposited at cathode will be
The reagent used for the preparation of higher ethers from halogenated ethers is
For which ore of the metal, froth floatation method is used for concentration?