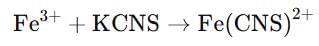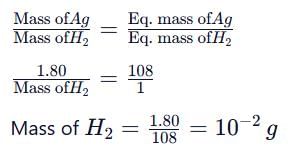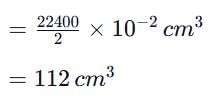VITEEE Chemistry Test - 1 - JEE MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - VITEEE Chemistry Test - 1
Ethyl alcohol on oxidation (Controlled oxidation) with K₂Cr₂O₇ gives
Which of the following compounds will undergo self aldol condensation in the presence of cold dilute alkali?
Which of the following reagent react differently with HCHO and CH₃CHO and CH₃COCH₃
Wurtz reaction involves the interaction of alkyl halides in dry ether with
The maximum amount of BaSO4 precipitated on mixing, the BaCl2 (0.5 M) with H2SO4(1 M) will correspond to:
Which of the following gives blood red colour with KCNS ?
A cylinder filled with a movable piston contains liquid water in equilibrium with water vapour at 25oC. Which one of the following operations results in a decreace in the equilibrium vapour pressure ?
Which one of the following is an example of exothermic reaction?
In the silver plating of copper, K[Ag(CN)₂] is used insead of AgNO₃. The reason is
Which of the following simple ions will not form complex ion with NH₃?
When quantity of electricity passed is one faraday then the mass deposited at the electrode is equal to
Electrode potentials (Eored) of 4 elements A,B,C,D are -1.36V, - 0.32V, 0V, -1.26 V respectively. The decreasing reactivity order of these elements is
Same amount of electric current is passed through solutions of AgNO₃ and HCI. If 1.08 g of silver is obtained in the first case, the volume of hydrogen liberated at S.T.P. in the second case is
When the densities of the ore particles and gangue particles are different, then the ore is concentrated by
The rate of diffusion of methane at a given temperature is twice that of a gas X. The molecular weight of X is