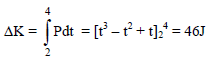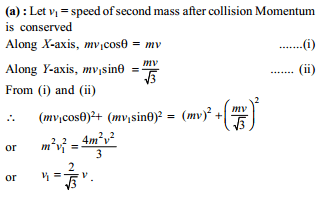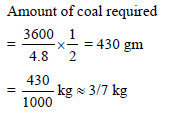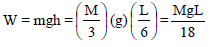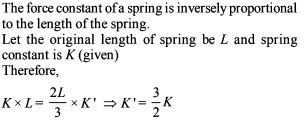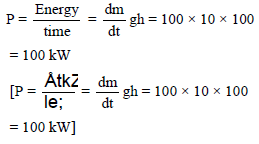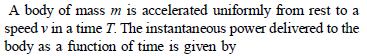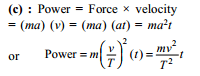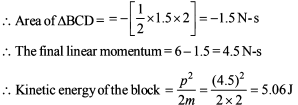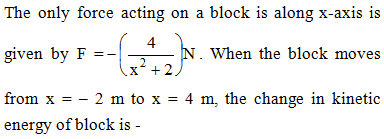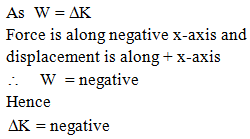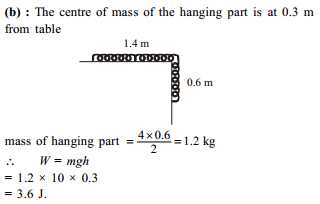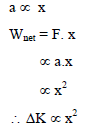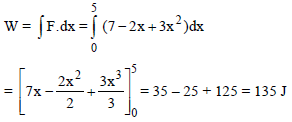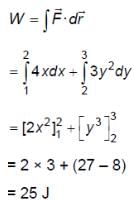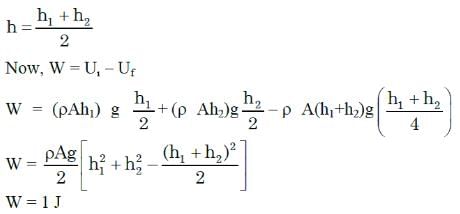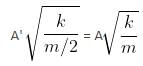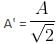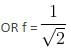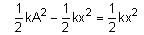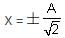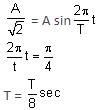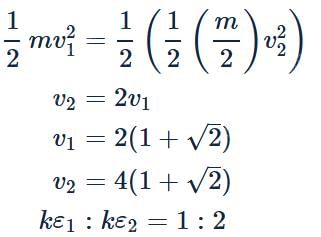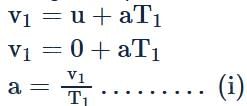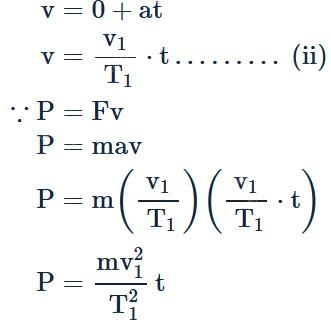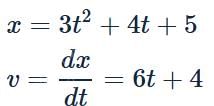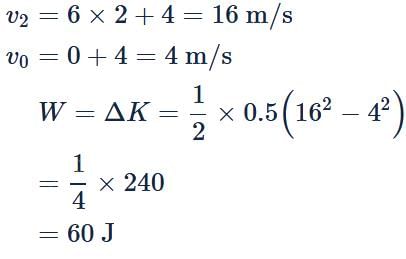Chapter Test: Work. Power & Energy - 1 - JEE MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test Physics for JEE Main & Advanced - Chapter Test: Work. Power & Energy - 1
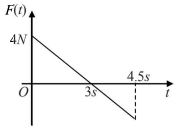
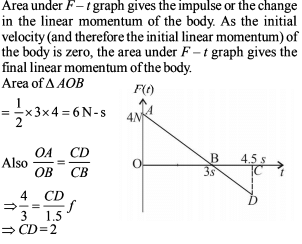
Power applied to a particle varies with time as P = [3t2 – 2t + 1] watts. Where t is time in seconds. Then the change in kinetic energy of particle between time t = 2s to t = 4s is –
By burning 1 g of coal, the energy produced is 2 kcal. Then for 1 kWh, the quantity of coal so required will be nearly -
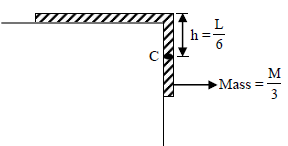
A uniform chain of length L and mass M is lying on a smooth table and one-third of its length is hanging vertically down over the edge of the table. If g is acceleration due to gravity, the work required to pull the hanging part on to the table is –
Water from a stream is falling on the blades of a turbine at the rate of 100 kg/sec. If the height of the stream is 100 m, then the power delivered to the turbine is -
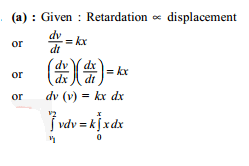
A particle moves in a straight line with its retardation proportional to its displacement 'x'. Change in kinetic energy is proportional to –
A particle moves along the x-axis from x = 0 to x = 5m under the influence of a force given by F = 7 – 2x + 3x2. The work done in the process is-
A particle experiences a variable force 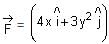 in a horizontal x-y plane. Assume distance in meters and force in newton. If the particle moves from point (1, 2) to point (2, 3) in the x-y plane; then kinetic energy changes by
in a horizontal x-y plane. Assume distance in meters and force in newton. If the particle moves from point (1, 2) to point (2, 3) in the x-y plane; then kinetic energy changes by
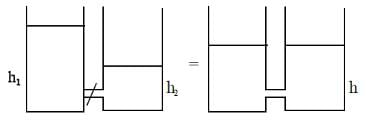
Two cylindrical vessels of equal cross-sectional area 16 cm2 contain water up to heights 100 cm and 150 cm, respectively. The vessels are interconnected so that the water levels in them become equal. The work done by the force of gravity during the process is: [Take density of water = 103 kg/m3 and g = 10 ms-2]
A block of mass m attached to a massless spring is performing oscillatory motion of amplitude 'A' on a frictionless horizontal plane. If half of the mass of the block breaks off when it is passing through its equilibrium point, the amplitude of oscillation for the remaining system become fA. The value of f is
A particle of mass 1 kg is hanging from a spring of force constant 100 Nm-1. The mass is pulled slightly downward and released, so that it executes free simple harmonic motion with time period T. The time when the kinetic energy and potential energy of the system will become equal is 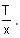 The value of x is _______. (in integers)
The value of x is _______. (in integers)
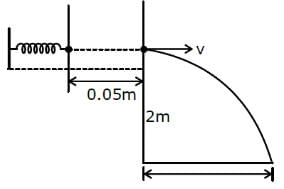
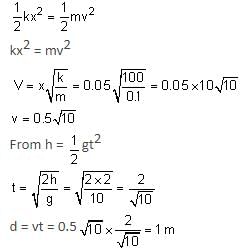
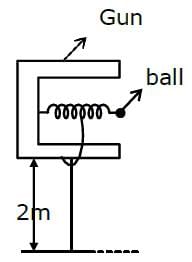
In a spring gun having spring constant 100 N/m, a small ball 'B' of mass 100 g is put in its barrel (as shown in figure) by compressing the spring through 0.05 m. There should be a box placed at a distance 'd' on the ground so that the ball falls in it. If the ball leaves the gun horizontally at a height of 2 m above the ground, the value of d is _______________ m.
(g = 10 m/s2) (in integers)
Two particles of masses m and 4m have linear momenta in the ratio of 2:1. What is the ratio of their kinetic energies?
A particle of mass m has half the kinetic energy of another particle of mass m/2. If the speed of the heavier particle is increased by 2 ms−1, its new kinetic energy equals the original kinetic energy of the lighter particle. The ratio of the original speeds of the lighter and heavier particles is
A body of mass m accelerates uniformly from rest to velocity v1 in time interval T1. The instantaneous power delivered to the body as a function of time t is:
The distance x moved by a body of mass 0.5 kg by a force varies with time t as x = 3t2 + 4t + 5 where x is expressed in metre and t in second. What is the work done by the force in the first 2 seconds?
|
297 videos|953 docs|172 tests
|