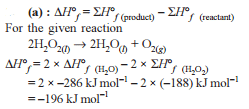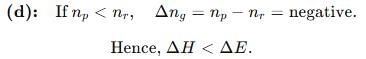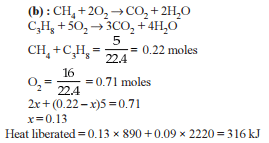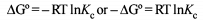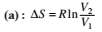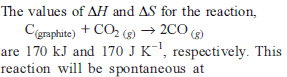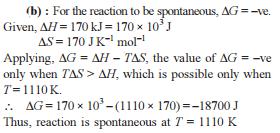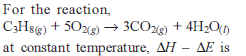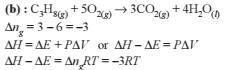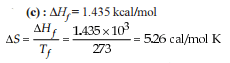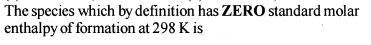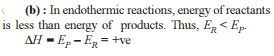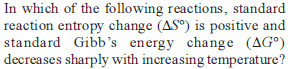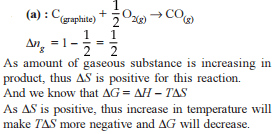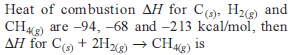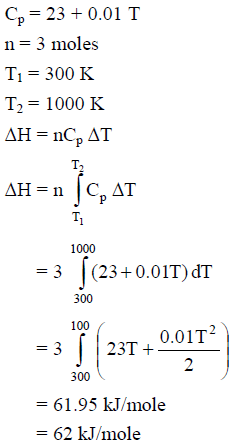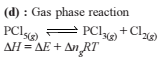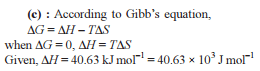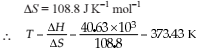Thermodynamics - 1 - JEE MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced - Thermodynamics - 1
The pressure-volume work for an ideal gas can be calculated using the expression
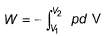
This type of work can also be calculated using the area under the curve within the specified limits. When an ideal gas is compressed, (I) reversibly or (II) irreversibly, then
In the following case, find the option with the correct matching
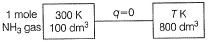
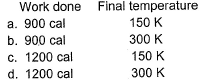
1.0 mole of a monoatomic ideal gas is expanded from state I to state II at 300 K.
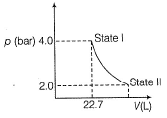
Thus, work done is
1 mole of a diatomic gas is contained in a piston. It gains 50.0 J of heat and work is done on the surrounding by the system is -100 J. Thus,
A sample containing 1.0 mole of an ideal gas is expanded isothermally and reversibly to ten time of its original volume, in two separate experiments. The expansion is carried out 300 K and at 600 K, respectively. Choose the correct option.
Change in enthalpy for reaction,
2H2O2(l) → 2H2O(l) + O2(g)
if heat of formation of H2O2(l) and H2O(l) are −188 and −286 kJ/mol respectively, is
If ΔH is the change in enthalpy and ΔE, the change in internal energy accompanying a gaseous reaction, then
During compression of a spring the work done is 10 kJ and 2 kJ escaped to the surroundings as heat. The change in internal energy, ΔU (in kJ) is :
Two moles of an ideal gas is expanded isothermally and reversibly from 1 litre to 10 litre at 300 K. The enthalpy change (in kJ) for the process is
When 5 litres of a gas mixture of methane and propane is perfectly combusted at 0°C and 1 atmosphere, 16 litres of oxygen at the same temperature and pressure is consumed. The amount of heat released from this combustion in kJ (ΔH_comb. (CH₄) = 890 kJ mol⁻¹, ΔH_comb. (C₃H₈) = 2220 kJ mol⁻¹) is
Consider the following reactions:
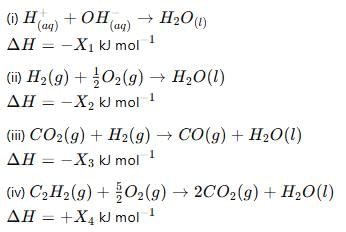
Enthalpy of formaton of H2O(l)
The correct relationship between free energy change in a reaction and the corresponding equilibrium constant
Kc is
For silver, Cp(JK–1 mol–1) = 23 + 0.01 T. If the temperature (T) of 3 moles of silver is raised from 300 K to 1000 K at 1 atm pressure, the value of ΔH will be close to -
|
361 videos|822 docs|301 tests
|