JEE Exam > JEE Tests > Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced > Biomolecules - 1 - JEE MCQ
Biomolecules - 1 - JEE MCQ
Test Description
20 Questions MCQ Test Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced - Biomolecules - 1
Biomolecules - 1 for JEE 2025 is part of Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced preparation. The Biomolecules - 1 questions and answers have been
prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus.The Biomolecules - 1 MCQs are made for JEE 2025 Exam. Find important
definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests for Biomolecules - 1 below.
Solutions of Biomolecules - 1 questions in English are available as part of our Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced for JEE & Biomolecules - 1 solutions in
Hindi for Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced course. Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock
test series for JEE Exam by signing up for free. Attempt Biomolecules - 1 | 20 questions in 20 minutes | Mock test for JEE preparation | Free important questions MCQ to study Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced for JEE Exam | Download free PDF with solutions
Detailed Solution for Biomolecules - 1 - Question 1
Biomolecules - 1 - Question 2
Insulin production and its action in human body are responsible for the level of diabetes. This compound belongs to which of the following categories ?
[AIEEE-2004]
Detailed Solution for Biomolecules - 1 - Question 2
Biomolecules - 1 - Question 3
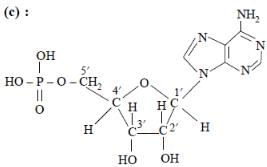
In both DNA and RNA, heterocylic base and phosphate ester linkages are at –
[AIEEE-2005]
Detailed Solution for Biomolecules - 1 - Question 3
Detailed Solution for Biomolecules - 1 - Question 4
Detailed Solution for Biomolecules - 1 - Question 5
Biomolecules - 1 - Question 6
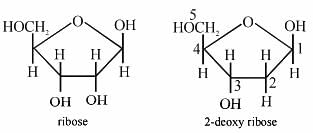
The presence or absence of hydroxyl group on which carbon atom of sugar differentiates RNA and DNA?
Detailed Solution for Biomolecules - 1 - Question 6
Biomolecules - 1 - Question 7
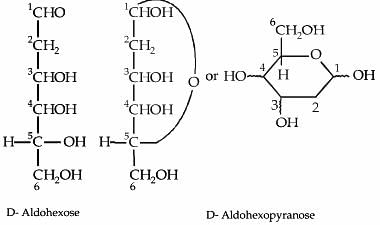
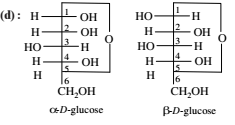
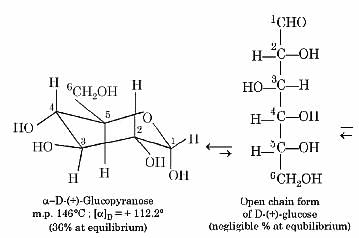
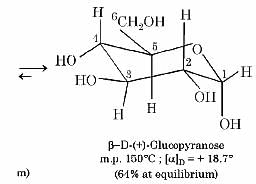
The two forms of D-glucopyranose obtained from the solution of D-glucose are called
Detailed Solution for Biomolecules - 1 - Question 7
Detailed Solution for Biomolecules - 1 - Question 8
Detailed Solution for Biomolecules - 1 - Question 9
Detailed Solution for Biomolecules - 1 - Question 10
Detailed Solution for Biomolecules - 1 - Question 11
Biomolecules - 1 - Question 12
When the following aldohexose exists in its D-configuration, the total number of stereoisomers in its pyranose form is:
CHO-CH₂-CHOH-CHOH-CHOH-CH₂OH
Detailed Solution for Biomolecules - 1 - Question 12
Detailed Solution for Biomolecules - 1 - Question 13
Detailed Solution for Biomolecules - 1 - Question 14
Detailed Solution for Biomolecules - 1 - Question 15
Detailed Solution for Biomolecules - 1 - Question 16
Detailed Solution for Biomolecules - 1 - Question 17
Biomolecules - 1 - Question 18
The α-D-glucose and β-D-glucose differ from each other due to difference in carbon atom with respect to its
Detailed Solution for Biomolecules - 1 - Question 18
Detailed Solution for Biomolecules - 1 - Question 19
Detailed Solution for Biomolecules - 1 - Question 20
|
361 videos|822 docs|301 tests
|
Information about Biomolecules - 1 Page
In this test you can find the Exam questions for Biomolecules - 1 solved & explained in the simplest way possible.
Besides giving Questions and answers for Biomolecules - 1, EduRev gives you an ample number of Online tests for practice